Iron homeostasis during cystic fibrosis pulmonary exacerbation
- PMID: 22883617
- PMCID: PMC3419499
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2012.00417.x
Iron homeostasis during cystic fibrosis pulmonary exacerbation
Abstract
Background: Hypoferremia is a marker of disease severity in cystic fibrosis (CF). The effect of systemic antibiotics on iron homeostasis during CF pulmonary exacerbation (CFPE) is unknown. Our central hypotheses were that, by the completion of treatment, serum iron would increase, serum concentrations of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and hepcidin-25, two mediators of hypoferremia, would decrease, and sputum iron would decrease.
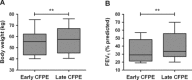
Methods: Blood and sputum samples were collected from 12 subjects with moderate-to-severe CF (median percentage-predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV(1) %) = 29%; median weight = 56 kg) within 24 hours of starting and completing a course of systemic antibiotics.
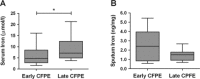
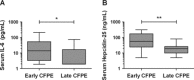
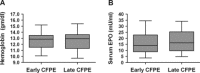
Results: After treatment, subjects showed median FEV(1) % and body weight improvements of 4.5% and 2.0 kg, respectively (p < 0.05). Median serum iron rose by 2.4 μmol/L (p < 0.05), but 75% of patients remained hypoferremic. Median serum IL-6 and hepcidin-25 levels fell by 12.1 pg/mL and 37.5 ng/mL, respectively (p < 0.05). Median serum erythropoietin (EPO) and hemoglobin levels were unaffected by treatment. We observed a trend toward lower sputum iron content after treatment.
Conclusions: Hypoferremia is a salient characteristic of CFPE that improves with waning inflammation. Despite antibiotic treatment, many patients remain hypoferremic and anemic because of ineffective erythropoiesis.
© 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott J, Holt A, Hart A, Morton AM, MacDougall L, Pogson M, Milne G, Rodgers HC, Conway SP. What defines a pulmonary exacerbation? The perceptions of adults with cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros. 2009; 8: 356–359. - PubMed
-
- Flume PA, Mogayzel PJ, Jr. , Robinson KA, Goss CH, Rosenblatt RL, Kuhn RJ, Marshall BC. Cystic fibrosis pulmonary guidelines: treatment of pulmonary exacerbations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009; 180: 802–808. - PubMed
-
- de Boer K, Vandemheen KL, Tullis E, Doucette S, Fergusson D, Freitag A, Paterson N, Jackson M, Lougheed MD, Kumar V, et al. Exacerbation frequency and clinical outcomes in adult patients with cystic fibrosis. Thorax. 2011; 66: 680–685. - PubMed
-
- Emerson J, Rosenfeld M, McNamara S, Ramsey B, Gibson RL. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other predictors of mortality and morbidity in young children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2002; 34: 91–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

