Muscleblind-like 2-mediated alternative splicing in the developing brain and dysregulation in myotonic dystrophy
- PMID: 22884328
- PMCID: PMC3418517
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.05.029
Muscleblind-like 2-mediated alternative splicing in the developing brain and dysregulation in myotonic dystrophy
Abstract
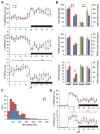
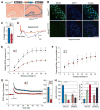
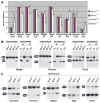
The RNA-mediated disease model for myotonic dystrophy (DM) proposes that microsatellite C(C)TG expansions express toxic RNAs that disrupt splicing regulation by altering MBNL1 and CELF1 activities. While this model explains DM manifestations in muscle, less is known about the effects of C(C)UG expression on the brain. Here, we report that Mbnl2 knockout mice develop several DM-associated central nervous system (CNS) features including abnormal REM sleep propensity and deficits in spatial memory. Mbnl2 is prominently expressed in the hippocampus and Mbnl2 knockouts show a decrease in NMDA receptor (NMDAR) synaptic transmission and impaired hippocampal synaptic plasticity. While Mbnl2 loss did not significantly alter target transcript levels in the hippocampus, misregulated splicing of hundreds of exons was detected using splicing microarrays, RNA-seq, and HITS-CLIP. Importantly, the majority of the Mbnl2-regulated exons examined were similarly misregulated in DM. We propose that major pathological features of the DM brain result from disruption of the MBNL2-mediated developmental splicing program.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Bailey TL, Elkan C. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol. 1994;2:28–36. - PubMed
-
- Bennett EJ, Shaler TA, Woodman B, Ryu KY, Zaitseva TS, Becker CH, Bates GP, Schulman H, Kopito RR. Global changes to the ubiquitin system in Huntington’s disease. Nature. 2007;448:704–708. - PubMed
-
- Ciafaloni E, Mignot E, Sansone V, Hilbert JE, Lin L, Lin X, Liu LC, Pigeon WR, Perlis ML, Thornton CA. The hypocretin neurotransmission system in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Neurology. 2008;70:226–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- K99GM95713/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG037984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG036800/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG036800/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG014979/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034389/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- GM084317/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS034389/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG037984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG037984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS34389/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS058901/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS058901/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000064/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM084317/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG014979/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR046799/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 GM095713/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 GM095713/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

