Using breast cancer cell CXCR4 surface expression to predict liposome binding and cytotoxicity
- PMID: 22884683
- PMCID: PMC3476061
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.07.043
Using breast cancer cell CXCR4 surface expression to predict liposome binding and cytotoxicity
Abstract
The primary cause of mortality in breast cancer is tumor aggressiveness, characterized by metastases to regional lymph nodes, bone marrow, lung, and liver. C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) has been shown to mobilize breast cancer cells along chemokine gradients. Quantification of CXCR4 surface expression may predict the efficacy of anti-CXCR4 labeled liposomal therapeutics to target and kill breast cancer cells. We evaluated gene and surface receptor expression of CXCR4 on breast cancer cell lines distinguished as having low and high invasiveness, MDA-MB-175VII and HCC1500, respectively. CXCR4 surface expression did not correlate with invasiveness. MDA-MB-175VII exhibited more binding to anti-CXCR4 labeled liposomes relative to HCC1500. Increased binding correlated with greater cell death relative to IgG labeled liposomes. Quantitative cell characterization may be used to select targeted therapeutics with enhanced efficacy and minimal side effects.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
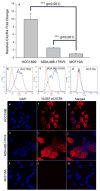
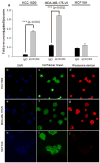
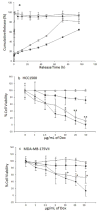
Similar articles
-
CXCR4-Targeted and Redox Responsive Dextrin Nanogel for Metastatic Breast Cancer Therapy.Biomacromolecules. 2017 Jun 12;18(6):1793-1802. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.7b00208. Epub 2017 May 10. Biomacromolecules. 2017. PMID: 28445650
-
Genetic manipulation of stromal cell-derived factor-1 attests the pivotal role of the autocrine SDF-1-CXCR4 pathway in the aggressiveness of breast cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2005 May;26(5):1429-34. Int J Oncol. 2005. PMID: 15809737
-
ITF2 is a target of CXCR4 in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells and is associated with reduced survival in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2010 Sep 15;10(6):600-14. doi: 10.4161/cbt.10.6.12586. Epub 2010 Sep 4. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20603605 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen-anchored pH-sensitive liposomes as nanomodule designed for site-specific delivery of doxorubicin in breast cancer therapy.Mol Pharm. 2012 Jan 1;9(1):176-86. doi: 10.1021/mp200439z. Epub 2011 Nov 28. Mol Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22091702
-
CXCR4 in breast cancer: oncogenic role and therapeutic targeting.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Aug 28;9:4953-64. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S84932. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26356032 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ICAM-1-Targeted, Lcn2 siRNA-Encapsulating Liposomes are Potent Anti-angiogenic Agents for Triple Negative Breast Cancer.Theranostics. 2016 Jan 1;6(1):1-13. doi: 10.7150/thno.12167. eCollection 2016. Theranostics. 2016. PMID: 26722369 Free PMC article.
-
An engineered bivalent neuregulin protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity with reduced proneoplastic potential.Circulation. 2013 Jul 9;128(2):152-61. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.002203. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Circulation. 2013. PMID: 23757312 Free PMC article.
-
Albumin-fatty acid interactions at monolayer interface.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2014 May 7;9(1):218. doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-9-218. eCollection 2014. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2014. PMID: 24910574 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Receptor-Mediated, Tumor-Targeted Drug Delivery.Adv Ther (Weinh). 2019 Jan;2(1):1800091. doi: 10.1002/adtp.201800091. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Adv Ther (Weinh). 2019. PMID: 38699509 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Targeted Liposome-based Chemotherapeutics to Treat Breast Cancer.Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2015 Aug 10;9(Suppl 2):1-5. doi: 10.4137/BCBCR.S29421. eCollection 2015. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2015. PMID: 26309409 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Cardoso F, Senkus-Konefka E, Fallowfield L, Costa A, Castiglione M. Locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2010;21:15–9. - PubMed
-
- Hickey RC, Gallager HS, Dodd GD, Samuels BI, Paulus DD, Jr, Moore DL. The detection and diagnosis of early, occult and minimal breast cancer. Adv Surg. 1976;10:287–312. - PubMed
-
- Weigelt B, Peterse JL, van't Veer LJ. Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:591–602. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, et al. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. New Engl J Med. 2001;344:783–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

