Deconstructing and reconstructing cognitive performance in sleep deprivation
- PMID: 22884948
- PMCID: PMC3498579
- DOI: 10.1016/j.smrv.2012.06.007
Deconstructing and reconstructing cognitive performance in sleep deprivation
Abstract
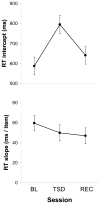
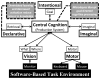
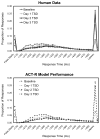
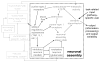
Mitigation of cognitive impairment due to sleep deprivation in operational settings is critical for safety and productivity. Achievements in this area are hampered by limited knowledge about the effects of sleep loss on actual job tasks. Sleep deprivation has different effects on different cognitive performance tasks, but the mechanisms behind this task-specificity are poorly understood. In this context it is important to recognize that cognitive performance is not a unitary process, but involves a number of component processes. There is emerging evidence that these component processes are differentially affected by sleep loss. Experiments have been conducted to decompose sleep-deprived performance into underlying cognitive processes using cognitive-behavioral, neuroimaging and cognitive modeling techniques. Furthermore, computational modeling in cognitive architectures has been employed to simulate sleep-deprived cognitive performance on the basis of the constituent cognitive processes. These efforts are beginning to enable quantitative prediction of the effects of sleep deprivation across different task contexts. This paper reviews a rapidly evolving area of research, and outlines a theoretical framework in which the effects of sleep loss on cognition may be understood from the deficits in the underlying neurobiology to the applied consequences in real-world job tasks.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Pilcher JJ, Huffcutt AJ. Effects of sleep deprivation on performance: a meta-analysis. Sleep. 1996;19:318–26. - PubMed
-
- Balkin T, Bliese P, Belenky G, Sing H, Thorne D, Thomas M, et al. Comparative utility of instruments for monitoring sleepiness-related performance decrements in the operational environment. J Sleep Res. 2004;13:219–27. - PubMed
-
- Jackson ML, Van Dongen HPA. Cognitive effects of sleepiness. In: Thorpy MJ, Billiard M, editors. Sleepiness. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 2011. pp. 72–81.
-
- Dinges DF. An overview of sleepiness and accidents. J Sleep Res. 1995;4(Suppl 2):4–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

