A specific role for septohippocampal acetylcholine in memory?
- PMID: 22884957
- PMCID: PMC3605586
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.07.022
A specific role for septohippocampal acetylcholine in memory?
Abstract
Acetylcholine has long been implicated in memory, including hippocampal-dependent memory, but the specific role for this neurotransmitter is difficult to identify in human neuropsychology. Here, we review the evidence for a mechanistic model of acetylcholine function within the hippocampus and consider its explanatory power for interpreting effects resulting from both pharmacological anticholinergic manipulations and lesions of the cholinergic input to the hippocampus in animals. We argue that these effects indicate that acetylcholine is necessary for some, but not all, hippocampal-dependent processes. We review recent evidence from lesion, pharmacological and electrophysiological studies to support the view that a primary function of septohippocampal acetylcholine is to reduce interference in the learning process by adaptively timing and separating encoding and retrieval processes. We reinterpret cholinergic-lesion based deficits according to this view and propose that acetylcholine reduces the interference elicited by the movement of salient locations between events.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
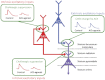

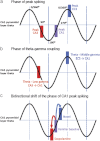

References
-
- Anagnostaras S.G., Maren S., Sage J.R., Goodrich S., Fanselow M.S. Scopolamine and Pavlovian fear conditioning in rats: dose-effect analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999;21(6):731–744. - PubMed
-
- Anderson M.I., Killing S., Morris C., O’Donoghue A., Onyiagha D., Stevenson R., Verriotis M., Jeffery K.J. Behavioral correlates of the distributed coding of spatial context. Hippocampus. 2006;16(9):730–742. - PubMed
-
- Atri A., Sherman S., Norman K.A., Kirchhoff B.A., Nicolas M.M., Greicius M.D., Cramer S.C., Breiter H.C., Hasselmo M.E., Stern C.E. Blockade of central cholinergic receptors impairs new learning and increases proactive interference in a word paired-associate memory task. Behavioral Neuroscience. 2004;118(1):223–236. - PubMed
-
- Barbeau E., Wendling F., Regis J., Duncan R., Poncet M., Chauvel P., Bartolomei F. Recollection of vivid memories after perirhinal region stimulations: synchronization in the theta range of spatially distributed brain areas. Neuropsychologia. 2005;43(9):1329–1337. - PubMed
-
- Baxter M.G., Bucci D.J., Sobel T.J., Williams M.J., Gorman L.K., Gallagher M. Intact spatial learning following lesions of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Neuroreport. 1996;7(8):1417–1420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

