Lysophosphatidic acid increases proximal tubule cell secretion of profibrotic cytokines PDGF-B and CTGF through LPA2- and Gαq-mediated Rho and αvβ6 integrin-dependent activation of TGF-β
- PMID: 22885106
- PMCID: PMC3463629
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.06.035
Lysophosphatidic acid increases proximal tubule cell secretion of profibrotic cytokines PDGF-B and CTGF through LPA2- and Gαq-mediated Rho and αvβ6 integrin-dependent activation of TGF-β
Abstract
After ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), kidney tubules show activated transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) signaling and increased expression of profibrotic peptides, platelet-derived growth factor-B (PDGF-B) and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF). If tubule repair after IRI is incomplete, sustained paracrine activity of these peptides can activate interstitial fibroblast progenitors and cause fibrosis. We show that lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), a ubiquitous phospholipid that is increased at sites of injury and inflammation, signals through LPA2 receptors and Gαq proteins of cultured proximal tubule cells to transactivate latent TGF-β in a Rho/Rho-kinase and αvβ6 integrin-dependent manner. Active TGF-β peptide then initiates signaling to increase the production and secretion of PDGF-B and CTGF. In a rat model of IRI, increased TGF-β signaling that was initiated early during reperfusion did not subside during recovery, but progressively increased, causing tubulointerstitial fibrosis. This was accompanied by correspondingly increased LPA2 and β6 integrin proteins and elevated tubule expression of TGF-β1, together with PDGF-B and CTGF. Treatment with a pharmacological TGF-β type I receptor antagonist suppressed TGF-β signaling, decreased the expression of β6 integrin, PDGF-B, and CTGF, and ameliorated fibrosis. We suggest that LPA-initiated autocrine signaling is a potentially important mechanism that gives rise to paracrine profibrotic signaling in injured kidney tubule cells.
Copyright © 2012 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
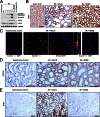
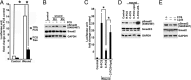
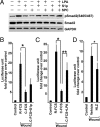
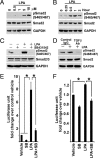
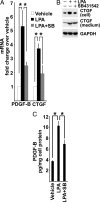
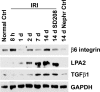
Comment in
-
TGF-β and renal fibrosis: a Pandora's box of surprises.Am J Pathol. 2012 Oct;181(4):1147-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.08.002. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Am J Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22921578 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Proximal tubule LPA1 and LPA2 receptors use divergent signaling pathways to additively increase profibrotic cytokine secretion.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021 Mar 1;320(3):F359-F374. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00494.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33427061 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophosphatidic acid induces alphavbeta6 integrin-mediated TGF-beta activation via the LPA2 receptor and the small G protein G alpha(q).Am J Pathol. 2009 Apr;174(4):1264-79. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080160. Epub 2009 Jan 15. Am J Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19147812 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β and renal fibrosis: a Pandora's box of surprises.Am J Pathol. 2012 Oct;181(4):1147-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.08.002. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Am J Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22921578 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in fibrosis and repair. Transforming growth factor-β activation by epithelial cells and fibroblasts.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015 Mar;12 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S21-3. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201406-245MG. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015. PMID: 25830829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting CTGF, EGF and PDGF pathways to prevent progression of kidney disease.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014 Dec;10(12):700-11. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2014.184. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 25311535 Review.
Cited by
-
Lysophosphatidic acid-induced RhoA signaling and prolonged macrophage infiltration worsens fibrosis and fatty infiltration following rotator cuff tears.J Orthop Res. 2017 Jul;35(7):1539-1547. doi: 10.1002/jor.23384. Epub 2016 Aug 19. J Orthop Res. 2017. PMID: 27505847 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between transforming growth factor β-2 and Autotaxin in trabecular meshwork and different subtypes of glaucoma.J Biomed Sci. 2021 Jun 17;28(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12929-021-00745-3. J Biomed Sci. 2021. PMID: 34140021 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-β1 and lysophosphatidic acid activate integrin β6 gene promoter in Hep-3B cells.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jul;16(1):439-446. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8672. Epub 2018 May 8. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29930716 Free PMC article.
-
Connective tissue growth factor and integrin αvβ6: a new pair of regulators critical for ductular reaction and biliary fibrosis in mice.Hepatology. 2015 Feb;61(2):678-91. doi: 10.1002/hep.27425. Hepatology. 2015. PMID: 25203810 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical chaperon 4-phenylbutyrate protects against the endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated renal fibrosis in vivo and in vitro.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 19;7(16):22116-27. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7904. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26959118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spurgeon K.R., Donohoe D.L., Basile D.P. Transforming growth factor-beta in acute renal failure: receptor expression, effects on proliferation, cellularity, and vascularization after recovery from injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005;288:F568–F577. - PubMed
-
- Geng H., Lan R., Wang G., Siddiqi A.R., Naski M.C., Brooks A.I., Barnes J.L., Saikumar P., Weinberg J.M., Venkatachalam M.A. Inhibition of autoregulated TGFbeta signaling simultaneously enhances proliferation and differentiation of kidney epithelium and promotes repair following renal ischemia. Am J Pathol. 2009;174:1291–1308. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basile D.P., Martin D.R., Hammerman M.R. Extracellular matrix-related genes in kidney after ischemic injury: potential role for TGF-beta in repair. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:F894–F903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

