A computational neurodegenerative disease progression score: method and results with the Alzheimer's disease Neuroimaging Initiative cohort
- PMID: 22885136
- PMCID: PMC3472161
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.07.059
A computational neurodegenerative disease progression score: method and results with the Alzheimer's disease Neuroimaging Initiative cohort
Abstract
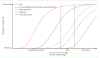
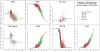
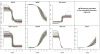
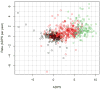
While neurodegenerative diseases are characterized by steady degeneration over relatively long timelines, it is widely believed that the early stages are the most promising for therapeutic intervention, before irreversible neuronal loss occurs. Developing a therapeutic response requires a precise measure of disease progression. However, since the early stages are for the most part asymptomatic, obtaining accurate measures of disease progression is difficult. Longitudinal databases of hundreds of subjects observed during several years with tens of validated biomarkers are becoming available, allowing the use of computational methods. We propose a widely applicable statistical methodology for creating a disease progression score (DPS), using multiple biomarkers, for subjects with a neurodegenerative disease. The proposed methodology was evaluated for Alzheimer's disease (AD) using the publicly available AD Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) database, yielding an Alzheimer's DPS or ADPS score for each subject and each time-point in the database. In addition, a common description of biomarker changes was produced allowing for an ordering of the biomarkers. The Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test delayed recall was found to be the earliest biomarker to become abnormal. The group of biomarkers comprising the volume of the hippocampus and the protein concentration amyloid beta and Tau were next in the timeline, and these were followed by three cognitive biomarkers. The proposed methodology thus has potential to stage individuals according to their state of disease progression relative to a population and to deduce common behaviors of biomarkers in the disease itself.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ashford J, Shan M, Butler S, Rajasekar A, Schmitt F. Temporal quantification of Alzheimer’s disease severity: ‘Time Index’ model. Dementia. 1995;6(5):269–280. - PubMed
-
- Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Arvanitakis Z, Kelly JF, Aggarwal NT, Shah RC, Wilson RS. Neuropathology of older persons without cognitive impairment from two community-based studies. Neurology. 2006;66(12):1837–1844. - PubMed
-
- Berg L, Miller JP, Storandt M, Duchek J, Morris JC, Rubin EH, Burke WJ, Coben LA. Mild senile dementia of the alzheimer type: 2. Longitudinal assessment. Annals of Neurology. 1988;23(5):477–484. - PubMed
-
- Brooks DJ, Pavese N. Imaging biomarkers in parkinson’s disease. Progress in Neurobiology. 2011 Aug; URL http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.08.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brooks J, 3rd, Kraemer H, Tanke E, Yesavage J. The methodology of studying decline in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 1993;41(6):623–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

