Lapatinib and potential prognostic value of EGFR mutations in a Gynecologic Oncology Group phase II trial of persistent or recurrent endometrial cancer
- PMID: 22885469
- PMCID: PMC3518448
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2012.07.127
Lapatinib and potential prognostic value of EGFR mutations in a Gynecologic Oncology Group phase II trial of persistent or recurrent endometrial cancer
Abstract
Objective: A phase II trial was performed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and HER2, lapatinib, and to explore EGFR, HER2 (EGFR2), phosphorylated ERK MAP kinase (pERK), and Ki67 expression, as well as EGFR mutations in persistent/recurrent endometrial cancer (EC).
Methods: Women with histologically-confirmed, measurable, persistent/recurrent EC following one or two prior regimens were eligible and treated with 1500 mg oral lapatinib daily until progression or severe toxicity. A 2-stage group sequential design was used to evaluate the regimen with 6 month PFS as the primary endpoint. The trial had a 10% type I error rate with 90% power. EGFR, HER2, pERK, and Ki67 were evaluated by immunohistochemistry (IHC) from hysterectomy specimens, pre-treatment biopsies, and post-treatment biopsies (when available). Exons 18-21 of EGFR were sequenced.
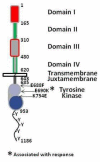
Results: Three patients of 30 evaluable had PFS ≥6 months, one had a partial response, seven had stable disease, 21 had progressive disease and one was indeterminate. Three mutations in EGFR were identified. Two of these, L688F and K754E, were not associated with response or PFS. However, a newly identified mutation in exon 18, E690K, occurred in the patient with a partial response and progression-free survival extending past six months.
Conclusion: While lapatinib has limited activity in unselected cases, the identification of a previously unreported mutation in EGFR (E690K) with a response suggests that lapatinib may be beneficial in some cases of EC.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Leslie KK, Laidler L, Albitar L, Davies S, Holmes A, Nguyen T, et al. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors in endometrial cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2005;15:409–11.
-
- Ebert AD, Wechselberger C, Martinez-Lacaci I, Bianco C, Weitzel HK, Salomon DS. Expression and function of EGF-related peptides and their receptors in gynecological cancer--from basic science to therapy. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2000;20:1–46. - PubMed
-
- Santin AD, Bellone S, Siegel ER, Palmieri M, Thomas M, Cannon MJ, et al. Racial differences in the overexpression of epidermal growth factor type II receptor (HER2/neu): a major prognostic indicator in uterine serous papillary cancer. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;192:813–8. - PubMed
-
- Benevolo M, Vocaturo A, Novelli F, Mariani L, Vocaturo G, Cianciulli AM, et al. Prognostic value of HER2 and progesterone receptor expression in endometrial carcinoma with positive peritoneal washing. Anticancer Res. 2007;27:2839–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

