Genome-wide association study of multiplex schizophrenia pedigrees
- PMID: 22885689
- PMCID: PMC6927206
- DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.11091423
Genome-wide association study of multiplex schizophrenia pedigrees
Abstract
Objective: The authors used a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of multiply affected families to investigate the association of schizophrenia to common single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and rare copy number variants (CNVs).
Method: The family sample included 2,461 individuals from 631 pedigrees (581 in the primary European-ancestry analyses). Association was tested for single SNPs and genetic pathways. Polygenic scores based on family study results were used to predict case-control status in the Schizophrenia Psychiatric GWAS Consortium (PGC) data set, and consistency of direction of effect with the family study was determined for top SNPs in the PGC GWAS analysis. Within-family segregation was examined for schizophrenia-associated rare CNVs.
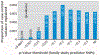
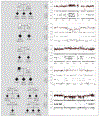
Results: No genome-wide significant associations were observed for single SNPs or for pathways. PGC case and control subjects had significantly different genome-wide polygenic scores (computed by weighting their genotypes by log-odds ratios from the family study) (best p=10(-17), explaining 0.4% of the variance). Family study and PGC analyses had consistent directions for 37 of the 58 independent best PGC SNPs (p=0.024). The overall frequency of CNVs in regions with reported associations with schizophrenia (chromosomes 1q21.1, 15q13.3, 16p11.2, and 22q11.2 and the neurexin-1 gene [NRXN1]) was similar to previous case-control studies. NRXN1 deletions and 16p11.2 duplications (both of which were transmitted from parents) and 22q11.2 deletions (de novo in four cases) did not segregate with schizophrenia in families.
Conclusions: Many common SNPs are likely to contribute to schizophrenia risk, with substantial overlap in genetic risk factors between multiply affected families and cases in large case-control studies. Our findings are consistent with a role for specific CNVs in disease pathogenesis, but the partial segregation of some CNVs with schizophrenia suggests that researchers should exercise caution in using them for predictive genetic testing until their effects in diverse populations have been fully studied.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Copy number variants in schizophrenia: confirmation of five previous findings and new evidence for 3q29 microdeletions and VIPR2 duplications.Am J Psychiatry. 2011 Mar;168(3):302-16. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2010.10060876. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Am J Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21285140 Free PMC article.
-
Copy number variation in schizophrenia in Sweden.Mol Psychiatry. 2014 Jul;19(7):762-73. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.40. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Mol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24776740 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study in a Swedish population yields support for greater CNV and MHC involvement in schizophrenia compared with bipolar disorder.Mol Psychiatry. 2012 Sep;17(9):880-6. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.73. Epub 2012 Jun 12. Mol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22688191 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic copy number variations: A breakthrough in our knowledge on schizophrenia etiology?Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2012;33(2):183-90. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22592199 Review.
-
A review of antipsychotic therapy effectiveness and tolerability among individuals with copy number variants relevant to schizophrenia.Psychiatr Genet. 2025 Jun 1;35(3):37-43. doi: 10.1097/YPG.0000000000000392. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Psychiatr Genet. 2025. PMID: 40145886 Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue-wide cell-specific proteogenomic modeling reveals novel candidate risk genes in autism spectrum disorders.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2022 Sep 6;8(1):31. doi: 10.1038/s41540-022-00243-8. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2022. PMID: 36068227 Free PMC article.
-
Neurexins.Genome Biol. 2013;14(9):213. doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-9-213. Genome Biol. 2013. PMID: 24083347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A scoring strategy combining statistics and functional genomics supports a possible role for common polygenic variation in autism.Front Genet. 2014 Feb 18;5:33. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00033. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 24600472 Free PMC article.
-
A matter of balance: role of neurexin and neuroligin at the synapse.Neurochem Res. 2013 Jun;38(6):1174-89. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1029-9. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 23559421 Review.
-
Recent Updates on Corticosteroid-Induced Neuropsychiatric Disorders and Theranostic Advancements through Gene Editing Tools.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jan 17;13(3):337. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13030337. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766442 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shi J, Levinson DF, Duan J, Sanders AR, Zheng Y, Pe’er I, Dudbridge F, Holmans PA, Whittemore AS, Mowry BJ, Olincy A, Amin F, Cloninger CR, Silverman JM, Buccola NG, Byerley WF, Black DW, Crowe RR, Oksenberg JR, Mirel DB, Kendler KS, Freedman R, Gejman PV: Common variants on chromosome 6p22.1 are associated with schizophrenia. Nature 2009; 460:753–757 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stefansson H, Ophoff RA, Steinberg S, Andreassen OA, Cichon S, Rujescu D, Werge T, Pietiläinen OP, Mors O, Mortensen PB, Sigurdsson E, Gustafsson O, Nyegaard M, Tuulio-Henriksson A, Ingason A, Hansen T, Suvisaari J, Lonnqvist J, Paunio T, Børglum AD, Hartmann A, Fink-Jensen A, Nordentoft M, Hougaard D, Norgaard-Pedersen B, Böttcher Y, Olesen J, Breuer R, Möller HJ, Giegling I, Rasmussen HB, Timm S, Mattheisen M, Bitter I, Réthelyi JM, Magnusdottir BB, Sigmundsson T, Olason P, Masson G, Gulcher JR, Haraldsson M, Fossdal R, Thorgeirsson TE, Thorsteinsdottir U, Ruggeri M, Tosato S, Franke B, Strengman E, Kiemeney LA, Melle I, Djurovic S, Abramova L, Kaleda V, Sanjuan J, de Frutos R, Bramon E, Vassos E, Fraser G, Ettinger U, Picchioni M, Walker N, Toulopoulou T, Need AC, Ge D, Yoon JL, Shianna KV, Freimer NB, Cantor RM, Murray R, Kong A, Golimbet V, Carracedo A, Arango C, Costas J, Jönsson EG, Terenius L, Agartz I, Petursson H, Nöthen MM, Rietschel M, Matthews PM, Muglia P, Peltonen L, St Clair D, Goldstein DB, Stefansson K, Collier DA: Genetic Risk and Outcome in Psychosis (GROUP): Common variants conferring risk of schizophrenia. Nature 2009; 460:744–747 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Håvik B, Le Hellard S, Rietschel M, Lybæk H, Djurovic S, Mattheisen M, Mühleisen TW, Degenhardt F, Priebe L, Maier W, Breuer R, Schulze TG, Agartz I, Melle I, Hansen T, Bramham CR, Nöthen MM, Stevens B, Werge T, Andreassen OA, Cichon S, Steen VM: The complement control-related genes CSMD1 and CSMD2 associate to schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2011; 70: 35–42 - PubMed
-
- Williams HJ, Norton N, Dwyer S, Moskvina V, Nikolov I, Carroll L, Georgieva L, Williams NM, Morris DW, Quinn EM, Giegling I, Ikeda M, Wood J, Lencz T, Hultman C, Lichtenstein P, Thiselton D, Maher BS, Malhotra AK, Riley B, Kendler KS, Gill M, Sullivan P, Sklar P, Purcell S, Nimgaonkar VL, Kirov G, Holmans P, Corvin A, Rujescu D, Craddock N, Owen MJ, O’Donovan MC: Molecular Genetics of Schizophrenia Collaboration (MGS) International Schizophrenia Consortium (ISC), SGENE-plus, GROUP: Fine mapping of ZNF804A and genome-wide significant evidence for its involvement in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2011; 16:429–441 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH061675/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH60879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59571/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH068922/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH068881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH61675/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059587/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH67257/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059586/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059566/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059588/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59566/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59587/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH60870/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59586/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH068881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH068921/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH067257/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH068922/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060870/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH062276/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059571/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059565/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH062276/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH068921/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59588/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0800509/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1000718/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

