Host protein BSL1 associates with Phytophthora infestans RXLR effector AVR2 and the Solanum demissum Immune receptor R2 to mediate disease resistance
- PMID: 22885736
- PMCID: PMC3462641
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.112.099861
Host protein BSL1 associates with Phytophthora infestans RXLR effector AVR2 and the Solanum demissum Immune receptor R2 to mediate disease resistance
Abstract
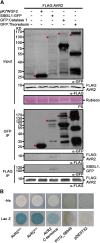
Plant pathogens secrete effector proteins to modulate plant immunity and promote host colonization. Plant nucleotide binding leucine-rich repeat (NB-LRR) immunoreceptors recognize specific pathogen effectors directly or indirectly. Little is known about how NB-LRR proteins recognize effectors of filamentous plant pathogens, such as Phytophthora infestans. AVR2 belongs to a family of 13 sequence-divergent P. infestans RXLR effectors that are differentially recognized by members of the R2 NB-LRR family in Solanum demissum. We report that the putative plant phosphatase BSU-LIKE PROTEIN1 (BSL1) is required for R2-mediated perception of AVR2 and resistance to P. infestans. AVR2 associates with BSL1 and mediates the interaction of BSL1 with R2 in planta, possibly through the formation of a ternary complex. Strains of P. infestans that are virulent on R2 potatoes express an unrecognized form, Avr2-like (referred to as A2l). A2L can still interact with BSL1 but does not promote the association of BSL1 with R2. Our findings show that recognition of the P. infestans AVR2 effector by the NB-LRR protein R2 requires the putative phosphatase BSL1. This reveals that, similar to effectors of phytopathogenic bacteria, recognition of filamentous pathogen effectors can be mediated via a host protein that interacts with both the effector and the NB-LRR immunoreceptor.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The cell biology of late blight disease.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016 Dec;34:127-135. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27723513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RXLR Effector AVR2 Up-Regulates a Brassinosteroid-Responsive bHLH Transcription Factor to Suppress Immunity.Plant Physiol. 2017 May;174(1):356-369. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.01804. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Plant Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28270626 Free PMC article.
-
Allelic variants of the NLR protein Rpi-chc1 differentially recognize members of the Phytophthora infestans PexRD12/31 effector superfamily through the leucine-rich repeat domain.Plant J. 2021 Jul;107(1):182-197. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15284. Epub 2021 May 29. Plant J. 2021. PMID: 33882622 Free PMC article.
-
AVR2 Targets BSL Family Members, Which Act as Susceptibility Factors to Suppress Host Immunity.Plant Physiol. 2019 May;180(1):571-581. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.01143. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Plant Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30782963 Free PMC article.
-
Effectors of Phytophthora pathogens are powerful weapons for manipulating host immunity.Planta. 2019 Aug;250(2):413-425. doi: 10.1007/s00425-019-03219-x. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Planta. 2019. PMID: 31243548 Review.
Cited by
-
The Meloidogyne graminicola effector Mg16820 is secreted in the apoplast and cytoplasm to suppress plant host defense responses.Mol Plant Pathol. 2018 Nov;19(11):2416-2430. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12719. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Mol Plant Pathol. 2018. PMID: 30011122 Free PMC article.
-
The Plant Membrane-Associated REMORIN1.3 Accumulates in Discrete Perihaustorial Domains and Enhances Susceptibility to Phytophthora infestans.Plant Physiol. 2014 Jul;165(3):1005-1018. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.235804. Epub 2014 May 7. Plant Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24808104 Free PMC article.
-
The cell biology of late blight disease.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016 Dec;34:127-135. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27723513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potato: from functional genomics to genetic improvement.Mol Hortic. 2024 Aug 19;4(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s43897-024-00105-3. Mol Hortic. 2024. PMID: 39160633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A potato STRUBBELIG-RECEPTOR FAMILY member, StLRPK1, associates with StSERK3A/BAK1 and activates immunity.J Exp Bot. 2018 Nov 26;69(22):5573-5586. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery310. J Exp Bot. 2018. PMID: 30137408 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belkhadir Y., Nimchuk Z., Hubert D.A., Mackey D., Dangl J.L. (2004). Arabidopsis RIN4 negatively regulates disease resistance mediated by RPS2 and RPM1 downstream or independent of the NDR1 signal modulator and is not required for the virulence functions of bacterial type III effectors AvrRpt2 or AvrRpm1. Plant Cell 16: 2822–2835 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benschop J.J., Mohammed S., O’Flaherty M., Heck A.J., Slijper M., Menke F.L. (2007). Quantitative phosphoproteomics of early elicitor signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 6: 1198–1214 - PubMed
-
- Bos J.I., Kanneganti T.D., Young C., Cakir C., Huitema E., Win J., Armstrong M.R., Birch P.R., Kamoun S. (2006). The C-terminal half of Phytophthora infestans RXLR effector AVR3a is sufficient to trigger R3a-mediated hypersensitivity and suppress INF1-induced cell death in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant J. 48: 165–176 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

