Large-scale association analysis provides insights into the genetic architecture and pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 22885922
- PMCID: PMC3442244
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2383
Large-scale association analysis provides insights into the genetic architecture and pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes
Abstract
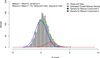
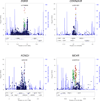
To extend understanding of the genetic architecture and molecular basis of type 2 diabetes (T2D), we conducted a meta-analysis of genetic variants on the Metabochip, including 34,840 cases and 114,981 controls, overwhelmingly of European descent. We identified ten previously unreported T2D susceptibility loci, including two showing sex-differentiated association. Genome-wide analyses of these data are consistent with a long tail of additional common variant loci explaining much of the variation in susceptibility to T2D. Exploration of the enlarged set of susceptibility loci implicates several processes, including CREBBP-related transcription, adipocytokine signaling and cell cycle regulation, in diabetes pathogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Stumvoll M, et al. Type 2 diabetes: principles of pathogenesis and therapy. Lancet. 2005;365:1333–1346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R56 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG04563/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- CZB/4/710/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- R01 DK073490/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CZB/4/672/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- 098017/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 DK058845/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GR098051/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- RG/08/008/25291/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- DK058845/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 HG000024/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UP_A100_1003/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 1R21NS064908/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- GR077016/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01HL59367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG10175/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HG065403/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085545/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G19/35/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- GR086596/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG2008/08/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0100222/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL059367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006513/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/08/014/24067/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- AG028555/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG008724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G8802774/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1000143/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- T32 HG000040/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- G0902037/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01HG004399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 1Z01HG000024/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DHCS/07/07/008/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- GR076113/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- GR084711/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106179471/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG028555/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 090367/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GR083270/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- GR081682/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0401527/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0701863/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K24 DK080140/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0000649/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- AG08861/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AG08724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0600717/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 064890/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N02HL64278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029887/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GR072960/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- UM1 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GR090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- DK073490/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS064908/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DK080140/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG010175/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RG/98002/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- U01 HG004399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 081682/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0601261/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- GR083948/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/07/008/23674/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

