Shigatoxin-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome: current molecular mechanisms and future therapies
- PMID: 22888220
- PMCID: PMC3414372
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S25757
Shigatoxin-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome: current molecular mechanisms and future therapies
Abstract
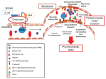
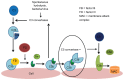
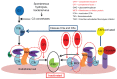
Hemolytic uremic syndrome is the leading cause of acute kidney injury in childhood. Ninety percent of cases are secondary to gastrointestinal infection with shigatoxin-producing bacteria. In this review, we discuss the molecular mechanisms of shigatoxin leading to hemolytic uremic syndrome and the emerging role of the complement system and vascular endothelial growth factor in its pathogenesis. We also review the evidence for treatment options to date, in particular antibiotics, plasma exchange, and immunoadsorption, and link this to the molecular pathology. Finally, we discuss future avenues of treatment, including shigatoxin-binding agents and complement inhibitors, such as eculizumab.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; alternative pathway; complement; diarrhea; eculizumab; hemolytic uremic syndrome; shigatoxin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Management of hemolytic uremic syndrome.Presse Med. 2012 Mar;41(3 Pt 2):e115-35. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2011.11.013. Epub 2012 Jan 27. Presse Med. 2012. PMID: 22284541
-
Is eculizumab efficacious in Shigatoxin-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome? A narrative review of current evidence.Eur J Pediatr. 2018 Mar;177(3):311-318. doi: 10.1007/s00431-017-3077-7. Epub 2017 Dec 29. Eur J Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 29288280 Review.
-
Hemolytic uremic syndrome: differential diagnosis with the onset of inflammatory bowel diseases.Acta Biomed. 2018 Dec 17;89(9-S):153-157. doi: 10.23750/abm.v89i9-S.7911. Acta Biomed. 2018. PMID: 30561409 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiology and treatment of typical and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome.Pathol Biol (Paris). 2015 Jun;63(3):136-43. doi: 10.1016/j.patbio.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 Apr 3. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2015. PMID: 25845294 Review.
-
Successful discontinuation of eculizumab therapy in a patient with aHUS.Ann Hematol. 2014 Aug;93(8):1423-5. doi: 10.1007/s00277-013-1972-1. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Ann Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24346709 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic plasma exchange in paediatric nephrology in Ireland.Ir J Med Sci. 2024 Jun;193(3):1589-1594. doi: 10.1007/s11845-023-03560-x. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Ir J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 37940814
-
Shiga Toxins: An Update on Host Factors and Biomedical Applications.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Mar 18;13(3):222. doi: 10.3390/toxins13030222. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Severely ill pediatric patients with Shiga toxin-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome (STEC-HUS) who suffered from multiple organ involvement in the early stage.Pediatr Nephrol. 2021 Jun;36(6):1499-1509. doi: 10.1007/s00467-020-04829-4. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Pediatr Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33205220
-
Fatal hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with day care surgery and anaesthesia: a case report.BMC Res Notes. 2013 Jun 26;6:242. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-6-242. BMC Res Notes. 2013. PMID: 23803463 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Shiga toxin with the A-domains and multimers of von Willebrand Factor.J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 15;288(46):33118-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.487413. Epub 2013 Oct 4. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24097977 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Garg AX, Suri RS, Barrowman N, et al. Long-term renal prognosis of diarrhea-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. JAMA. 2003;290:1360–1370. - PubMed
-
- Ake JA, Jelacic S, Ciol MA, et al. Relative nephroprotection during Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections: association with intravenous volume expansion. Pediatrics. 2005;115:e673–e680. - PubMed
-
- Verweyen HM, Karch H, Brandis M, Zimmerhackl LB. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli infections: following transmission routes. Pediatr Nephrol. 2000;14:73–83. - PubMed
-
- Noris M, Remuzzi G. Hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:1035–1050. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

