Parental persuasive strategies in the face of daily problems in adolescent type 1 diabetes management
- PMID: 22888825
- PMCID: PMC8530460
- DOI: 10.1037/a0029427
Parental persuasive strategies in the face of daily problems in adolescent type 1 diabetes management
Abstract
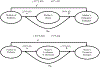
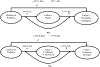
Objective: The study examined (1) whether daily diabetes problems that adolescents experience were associated with parental persuasive strategies (e.g., persuading the adolescent to do more to manage diabetes), (2) whether this association was mediated through greater parental worry and lower confidence in adolescents' abilities, and (3) how parental persuasive strategies may provide corrections for subsequent blood glucose control but reduce adolescent confidence for adolescents high in self-efficacy.
Method: Adolescents with Type 1 diabetes (N = 180, ages 10.50-15.58 years) and their mothers (N = 176) and fathers (N = 139) completed diaries for 14 days reporting on problems experienced with diabetes, maternal and paternal use of persuasive strategies, and confidence in adolescents' ability to manage diabetes. Parents reported their daily worry about diabetes, adolescents reported their general self-efficacy for diabetes management, and blood glucose was downloaded from glucometers.
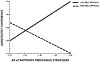
Results: Across reporters, multilevel modeling revealed that parents used more persuasive strategies on days when more diabetes problems were experienced. This association was mediated through parents' greater worry and lower confidence in adolescents' ability to manage diabetes. Lagged analyses revealed that adolescents' perceptions of maternal persuasive strategies were associated with improvements in next-day blood glucose, but also with reductions in adolescents' daily confidence for those high in self-efficacy.
Conclusions: Parental persuasive strategies appear responsive to daily problems that adolescents experience in diabetes management. Mothers' persuasive strategies may have the dual effects of correcting blood glucose levels but reducing the more self-efficacious adolescents' confidence in their own ability to manage diabetes.
PsycINFO Database Record (c) 2013 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson BJ, & Coyne JC (1991). “Miscarried helping” in the families of children and adolescents with chronic diseases. In Johnson JH & Johnson SB (Eds.), Advances in child health psychology (pp. 167–177). Gainesville, FL: University of Florida.
-
- Anderson BJ, Holmbeck G, Iannotti RJ, McKay SV, Lochrie A, Volkening LK, & Laffel LK (2009). Dyadic measures of the parent–child relationship during the transition to adolescence and glycemic control in children with type 1 diabetes. Families, Systems, & Health, 27, 141–152. doi:10.1037/a0015759 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

