Seminal vesicle interfraction displacement and margins in image guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer
- PMID: 22889144
- PMCID: PMC3487760
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-7-139
Seminal vesicle interfraction displacement and margins in image guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer
Abstract
Background: To analyze interfraction motion of seminal vesicles (SV), and its motion relative to rectal and bladder filling.
Methods and materials: SV and prostate were contoured on 771 daily computed tomography "on rails" scans from 24 prostate cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy. Random and systematic errors for SV centroid displacement were measured relative to the prostate centroid. Margins required for complete geometric coverage of SV were determined using isotropic expansion of reference contours. SV motion relative to rectum and bladder was determined.
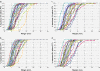
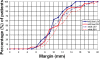
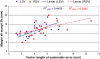
Results: Systematic error for the SV was 1.9 mm left-right (LR), 2.9 mm anterior-posterior (AP) and 3.6 mm superior-inferior (SI). Random error was 1.4 mm (LR), 2.7 mm (AP) and 2.1 mm (SI). 10 mm margins covered the entire left SV and right SV on at least 90% of fractions in 50% and 33% of patients and 15 mm margins covered 88% and 79% respectively. SV AP movement correlated with movement of the most posterior point of the bladder (mean R2 = 0.46, SD = 0.24) and rectal area (mean R2 = 0.38, SD = 0.21).
Conclusions: Considerable interfraction displacement of SV was observed in this cohort of patients. Bladder and rectal parameters correlated with SV movement.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Quantification and predictors of prostate position variability in 50 patients evaluated with multiple CT scans during conformal radiotherapy.Radiother Oncol. 1999 Feb;50(2):225-34. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(99)00011-0. Radiother Oncol. 1999. PMID: 10368047
-
A critical evaluation of the planning target volume for 3-D conformal radiotherapy of prostate cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998 Aug 1;42(1):213-21. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(98)00189-8. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998. PMID: 9747840
-
Dosimetric implications of residual seminal vesicle motion in fiducial-guided intensity-modulated radiotherapy for prostate cancer.Med Dosim. 2012 Autumn;37(3):240-4. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2011.09.002. Epub 2011 Dec 19. Med Dosim. 2012. PMID: 22189029
-
Seminal vesicle inter- and intra-fraction motion during radiotherapy for prostate cancer: A review.Radiother Oncol. 2022 Apr;169:15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2022.02.002. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Radiother Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35157975 Review.
-
Development of RTOG consensus guidelines for the definition of the clinical target volume for postoperative conformal radiation therapy for prostate cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010 Feb 1;76(2):361-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.02.006. Epub 2009 Apr 23. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010. PMID: 19394158 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Optimal Bladder Volume for Hypofractionated Proton Therapy in Each Localized Prostate Cancer Risk Group.Cureus. 2023 Nov 13;15(11):e48723. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48723. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38094565 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of delivered dose in prostate cancer patients treated with ultra-hypofractionated radiotherapy on 1.5-Tesla MR-Linac.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 19;13:1039901. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1039901. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36741014 Free PMC article.
-
Take Action Protocol: A radiation therapist led approach to act on anatomical changes seen on CBCT.Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2021 Mar 18;17:71-77. doi: 10.1016/j.tipsro.2020.12.001. eCollection 2021 Mar. Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34007910 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging-guided radiotherapy for intermediate- and high-risk prostate cancer: Trade-off between planning target volume margin and online plan adaption.Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2022 Jul 3;23:92-96. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2022.06.013. eCollection 2022 Jul. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35844255 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of hydrogel rectal spacer on seminal vesicle inter-fraction motion during prostate stereotactic body radiotherapy.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 2;15(1):19261. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04475-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40456845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gluck I, Vineberg KA, Ten Haken RK, Sandler HM. Evaluating the relationships between rectal normal tissue complication probability and the portion of seminal vesicles included in the clinical target volume in intensity-modulated radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;73:334–340. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.09.025. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

