Pharmacological effects of 3-iodothyronamine (T1AM) in mice include facilitation of memory acquisition and retention and reduction of pain threshold
- PMID: 22889145
- PMCID: PMC3572562
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02137.x
Pharmacological effects of 3-iodothyronamine (T1AM) in mice include facilitation of memory acquisition and retention and reduction of pain threshold
Abstract
Background and purpose: 3-Iodothyronamine (T1AM), an endogenous derivative of thyroid hormones, is regarded as a rapid modulator of behaviour and metabolism. To determine whether brain thyroid hormone levels contribute to these effects, we investigated the effect of central administration of T1AM on learning and pain threshold of mice either untreated or pretreated with clorgyline (2.5 mg·kg(-1) , i.p.), an inhibitor of amine oxidative metabolism.
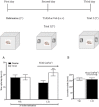
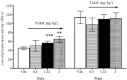
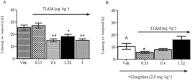
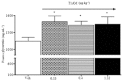
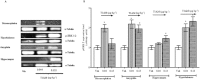
Experimental approach: T1AM (0.13, 0.4, 1.32 and 4 μg·kg(-1) ) or vehicle was injected i.c.v. into male mice, and after 30 min their effects on memory acquisition capacity, pain threshold and curiosity were evaluated by the following tests: passive avoidance, licking latency on the hot plate and movements on the hole-board platform. Plasma glycaemia was measured using a glucorefractometer. Brain levels of triiodothyroxine (T3), thyroxine (T4) and T1AM were measured by HPLC coupled to tandem MS. ERK1/2 activation and c-fos expression in different brain regions were evaluated by Western blot analysis.
Results: T1AM improved learning capacity, decreased pain threshold to hot stimuli, enhanced curiosity and raised plasma glycaemia in a dose-dependent way, without modifying T3 and T4 brain concentrations. T1AM effects on learning and pain were abolished or significantly affected by clorgyline, suggesting a role for some metabolite(s), or that T1AM interacts at the rapid desensitizing target(s). T1AM activated ERK in different brain areas at lower doses than those effective on behaviour.
Conclusions and implications: T1AM is a novel memory enhancer. This feature might have important implications for the treatment of endocrine and neurodegenerative-induced memory disorders.
© 2012 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2012 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Bauer M, Goetz T, Glenn T, Whybrow PC. The thyroid-brain interaction in thyroid disorders and mood disorders. J Neuroendocrinol. 2008;20:1101–1114. - PubMed
-
- Dhillo WS, Bewick GA, White NE, Gardiner JV, Thompson EL, Bataveljic A, et al. The thyroid hormone derivative 3-iodothyronamine increases food intake in rodents. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008;11:251–260. - PubMed
-
- Doyle KP, Suchland KL, Ciesielski TM, Lessov NS, Grandy DK, Scanlan TS, et al. Novel thyroxine derivatives, thyronamine and 3-iodothyronamine, induce transient hypothermia and marked neuroprotection against stroke injury. Stroke. 2007;38:2569–2576. - PubMed
-
- Ennaceur A, Delacour J. A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: behavioral data. Behav Brain Res. 1988;31:47–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

