Effect of muscle load tasks with maximal isometric contractions on oxygenation of the trapezius muscle and sympathetic nervous activity in females with chronic neck and shoulder pain
- PMID: 22889146
- PMCID: PMC3543720
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-13-146
Effect of muscle load tasks with maximal isometric contractions on oxygenation of the trapezius muscle and sympathetic nervous activity in females with chronic neck and shoulder pain
Abstract
Background: Sympathetic nervous activity contributes to the maintenance of muscle oxygenation. However, patients with chronic pain may suffer from autonomic dysfunction. Furthermore, insufficient muscle oxygenation is observed among workers with chronic neck and shoulder pain. The aim of our study was to investigate how muscle load tasks affect sympathetic nervous activity and changes in oxygenation of the trapezius muscles in subjects with chronic neck and shoulder pain.
Methods: Thirty females were assigned to two groups: a pain group consisting of subjects with chronic neck and shoulder pain and a control group consisting of asymptomatic subjects. The participants performed three sets of isometric exercise in an upright position; they contracted their trapezius muscles with maximum effort and let the muscles relax (Relax). Autonomic nervous activity and oxygenation of the trapezius muscles were measured by heart rate variability (HRV) and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy.
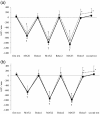
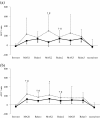
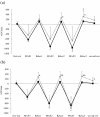
Results: Oxyhemoglobin and total hemoglobin of the trapezius muscles in the pain group were lower during the Relax period compared with the control group. In addition, the low frequency / high frequency (LF/HF) ratio of HRV significantly increased during isometric exercise in the control group, whereas there were no significant changes in the pain group.
Conclusions: Subjects with neck and shoulder pain showed lower oxygenation and blood flow of the trapezius muscles responding to isometric exercise, compared with asymptomatic subjects. Subjects with neck and shoulder pain also showed no significant changes in the LF/HF ratio of HRV responding to isometric exercise, which would imply a reduction in sympathetic nervous activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of cycling on oxygenation of relaxed neck/shoulder muscles in women with and without chronic pain.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010 Sep;110(2):389-94. doi: 10.1007/s00421-010-1517-4. Epub 2010 May 29. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20512501 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of static contraction and cold stimulation on cardiovascular autonomic indices, trapezius blood flow and muscle activity in chronic neck-shoulder pain.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011 Aug;111(8):1725-35. doi: 10.1007/s00421-010-1813-z. Epub 2011 Jan 9. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21221987 Clinical Trial.
-
Ultrasonographic analysis of dorsal neck muscles thickness changes induced by isometric contraction of shoulder muscles: A comparison between patients with chronic neck pain and healthy controls.Man Ther. 2016 Apr;22:174-8. doi: 10.1016/j.math.2015.12.004. Epub 2015 Dec 22. Man Ther. 2016. PMID: 26797174
-
Lower trapezius muscle function in people with and without shoulder and neck pain: a systematic review.J Osteopath Med. 2022 Sep 13;123(2):73-89. doi: 10.1515/jom-2022-0056. eCollection 2023 Jan 1. J Osteopath Med. 2022. PMID: 36100364
-
Chronic Pain-Associated Cardiovascular Disease: The Role of Sympathetic Nerve Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 11;24(6):5378. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065378. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Term Monitoring of Physical Behavior Reveals Different Cardiac Responses to Physical Activity among Subjects with and without Chronic Neck Pain.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:907482. doi: 10.1155/2015/907482. Epub 2015 Oct 18. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26557711 Free PMC article.
-
High-Intensity Static Stretching in Quadriceps Is Affected More by Its Intensity Than Its Duration.Front Physiol. 2021 Jul 5;12:709655. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.709655. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34290625 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging of muscle and adipose tissue in the spine: A narrative review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Dec 9;101(49):e32051. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032051. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36626484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autonomic responses to aerobic and resistance exercise in patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 14;18(8):e0290061. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290061. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37578955 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of High Intensity 20-Second Static Stretching on the Flexibility and Strength of Hamstrings.J Sports Sci Med. 2020 May 1;19(2):429-435. eCollection 2020 Jun. J Sports Sci Med. 2020. PMID: 32390737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fredriksson K, Alfredsson L, Ahlberg G, Josephson M, Kilbom A, Wigaeus Hjelm E, Wiktorin C, Vingard E. Work encironment and neck and shoulder pain: the influence of exposure time. Results from a population based case–control study. Occup Enciron Med. 2002;59:182–188. doi: 10.1136/oem.59.3.182. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Larsson B, Björk J, Henriksson KG, Gerdle B, Lindman R. The prevalences of cytochrome oxidase negative and superpositive fibres and ragged-red fibres in the trapezius muscle of female cleaners with and without myalgia and of female healthy controls. Pain. 2000;84:379–387. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3959(99)00237-7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

