X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD): clinical presentation and guidelines for diagnosis, follow-up and management
- PMID: 22889154
- PMCID: PMC3503704
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1172-7-51
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD): clinical presentation and guidelines for diagnosis, follow-up and management
Abstract
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) is the most common peroxisomal disorder. The disease is caused by mutations in the ABCD1 gene that encodes the peroxisomal membrane protein ALDP which is involved in the transmembrane transport of very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA; ≥ C22). A defect in ALDP results in elevated levels of VLCFA in plasma and tissues. The clinical spectrum in males with X-ALD ranges from isolated adrenocortical insufficiency and slowly progressive myelopathy to devastating cerebral demyelination. The majority of heterozygous females will develop symptoms by the age of 60 years. In individual patients the disease course remains unpredictable. This review focuses on the diagnosis and management of patients with X-ALD and provides a guideline for clinicians that encounter patients with this highly complex disorder.
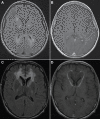
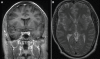
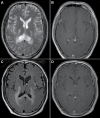
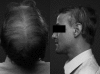
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

