Inhibitory effects of pepstatin A and mefloquine on the growth of Babesia parasites
- PMID: 22890034
- PMCID: PMC3516319
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.2012.12-0218
Inhibitory effects of pepstatin A and mefloquine on the growth of Babesia parasites
Abstract
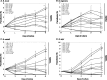
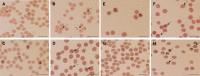
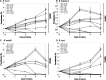
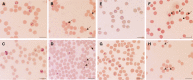
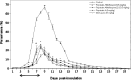
We evaluated the inhibitory effects of pepstatin A and mefloquine on the in vitro and in vivo growths of Babesia parasites. The in vitro growth of Babesia bovis, B. bigemina, B. caballi, and B. equi was significantly inhibited (P < 0.05) by micromolar concentrations of pepstatin A (50% inhibitory concentrations = 38.5, 36.5, 17.6, and 18.1 μM, respectively) and mefloquine (50% inhibitory concentrations = 59.7, 56.7, 20.7, and 4 μM, respectively). Furthermore, both reagents either alone at a concentration of 5 mg/kg or in combinations (2.5/2.5 and 5/5 mg/kg) for 10 days significantly inhibited the in vivo growth of B. microti in mice. Mefloquine treatment was highly effective and the combination treatments were less effective than other treatments. Therefore, mefloquine may antagonize the actions of pepstatin A against babesiosis and aspartic proteases may play an important role in the asexual growth cycle of Babesia parasites.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effect of terpene nerolidol on the growth of Babesia parasites.Parasitol Int. 2010 Jun;59(2):278-82. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2010.02.006. Epub 2010 Feb 21. Parasitol Int. 2010. PMID: 20178862
-
Effect of protease inhibitors on the intraerythrocytic development of Babesia microti and Babesia duncani, the causative agents of human babesiosis.J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2025 Mar-Apr;72(2):e13064. doi: 10.1111/jeu.13064. Epub 2024 Nov 18. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39556081 Free PMC article.
-
Ellagic acid microspheres restrict the growth of Babesia and Theileria in vitro and Babesia microti in vivo.Parasit Vectors. 2019 May 28;12(1):269. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3520-x. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31138282 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Bioinformatics Analysis of Transcription Factor Genes Indicates Conservation of Key Regulatory Domains among Babesia bovis, Babesia microti, and Theileria equi.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 Nov 10;10(11):e0004983. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004983. eCollection 2016 Nov. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016. PMID: 27832060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assay methods for in vitro and in vivo anti-Babesia drug efficacy testing: Current progress, outlook, and challenges.Vet Parasitol. 2020 Mar;279:109013. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2019.109013. Epub 2019 Dec 13. Vet Parasitol. 2020. PMID: 32070899 Review.
Cited by
-
Bumped kinase inhibitor prohibits egression in Babesia bovis.Vet Parasitol. 2016 Jan 15;215:22-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2015.10.023. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Vet Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 26790733 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Efficacy of Longer versus Shorter Pulsed High Dose Dapsone Combination Therapy in the Treatment of Chronic Lyme Disease/Post Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome with Bartonellosis and Associated Coinfections.Microorganisms. 2023 Sep 12;11(9):2301. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11092301. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37764145 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic drug combination effectively blocks Ebola virus infection.Antiviral Res. 2017 Jan;137:165-172. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.11.017. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Antiviral Res. 2017. PMID: 27890675 Free PMC article.
-
Alsinol, an arylamino alcohol derivative active against Plasmodium, Babesia, Trypanosoma, and Leishmania: past and new outcomes.Parasitol Res. 2020 Oct;119(10):3503-3515. doi: 10.1007/s00436-020-06832-y. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Parasitol Res. 2020. PMID: 32772176
-
Evaluation of possible prophylactic and therapeutic effect of mefloquine on experimental cryptosporidiosis in immunocompromised mice.J Parasit Dis. 2021 Jun;45(2):380-393. doi: 10.1007/s12639-020-01315-4. Epub 2020 Nov 13. J Parasit Dis. 2021. PMID: 34295037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuttler KL. World-wide impact of babesiosis. In: Ristic M, editor. Babesiosis of Domestic Animals and Man. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 1988. pp. 1–22.
-
- Wright IG, Goodger BV. Pathogenesis of babesiosis. In: Ristic M, editor. Babesiosis of Domestic Animals and Man. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 1988. pp. 99–118.
-
- Kjemtrup AM, Conrad PA. Human babesiosis: an emerging tick-borne disease. Int J Parasitol. 2000;30:1323–1337. - PubMed
-
- Vial HJ, Gorenflot A. Chemotherapy against babesiosis. Vet Parasitol. 2006;138:147–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

