The nuclear factor erythroid 2-like 2 activator, tert-butylhydroquinone, improves cognitive performance in mice after mild traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 22890082
- PMCID: PMC9150436
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.07.070
The nuclear factor erythroid 2-like 2 activator, tert-butylhydroquinone, improves cognitive performance in mice after mild traumatic brain injury
Abstract
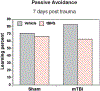
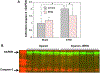
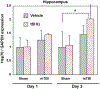
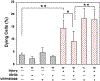
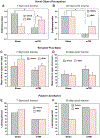
Traumatic Brain injury affects at least 1.7 million people in the United States alone each year. The majority of injuries are categorized as mild but these still produce lasting symptoms that plague the patient and the medical field. Currently treatments are aimed at reducing a patient's symptoms, but there is no effective method to combat the source of the problem, neuronal loss. We tested a mild, closed head traumatic brain injury model for the effects of modulation of the antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2 by the chemical activator, tert-butylhydroquinone (tBHQ). We found that post-injury visual memory was improved by a 7 day course of treatment and that the level of activated caspase-3 in the hippocampus was reduced. The injury-induced memory loss was also reversed by a single injection at 30 min after injury. Since the protective stress response molecule, HSP70, can be upregulated by Nrf2, we examined protein levels in the hippocampus, and found that HSP70 was elevated by the injury and then further increased by the treatment. To test the possible role of HSP70, model neurons in culture exposed to a mild injury and treated with the Nrf2 activator displayed improved survival that was blocked by the HSP70 inhibitor, VER155008. Following mild traumatic brain injury, there may be a partial protective response and patients could benefit from directed enhancement of regulatory pathways such as Nrf2 for neuroprotection.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

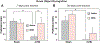

References
-
- Abramoff MD, Mgalhaes PJ, Ram SJ (2004) Image processing with ImageJ. Biophoton Intl 11:36–42.
-
- Bazarian JJ, Zhong J, Blyth B, Zhu T, Kavcic V, Peterson D (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging detects clinically important axonal damage after mild traumatic brain injury: a pilot study. J Neurotrauma 24:1447–1459. - PubMed
-
- Beere HM, Wolf BB, Cain K, Mosser DD, Mahboubi A, Kuwana T, Tailor P, Morimoto RI, Cohen GM, Green DR (2000) Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat Cell Biol 2:469–475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

