Disease recurrence in sentinel node-positive breast cancer patients forgoing axillary lymph node dissection
- PMID: 22890591
- PMCID: PMC4043293
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-012-2547-4
Disease recurrence in sentinel node-positive breast cancer patients forgoing axillary lymph node dissection
Abstract
Background: Clinically node-negative breast cancer patients usually undergo sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy. When metastasis is identified, completion axillary lymph node dissection (CALND) is recommended. Newer data suggest that CALND may be omitted in some women as it does not improve local control or survival.
Methods: Women with a positive SLN diagnosed between 1999 and 2010 were included in this review and were stratified according to whether they did or did not undergo CALND. Primary endpoints included recurrence and breast cancer-specific mortality. Differences between the groups and in time to recurrence were compared and summarized.
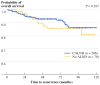
Results: Overall, 276 women were included: 206 (79 %) women who underwent CALND (group 1) and 70 (21 %) women in whom CALND was omitted (group 2). Group 1 patients were younger, had more SLN disease, and received more chemotherapy (P < 0.05 for each). The groups did not vary by tumor characteristics (P > 0.05 for each). Median follow-up was 69 (range 6-147) and 73 (range 15-134) months for groups 1 and 2, respectively. Five (2 %) women in group 1 and three (4 %) women in group 2 died of breast cancer (P = 0.39). Local-regional or distant recurrence occurred in 20 (10 %) group 1 patients and in 10 (14 %) group 2 patients (P = 0.39). On multivariate analysis, only estrogen receptor negativity and lymphovascular invasion predicted for recurrence.
Conclusions: Omission of CALND in women with SLN disease does not significantly impact in-breast, nodal, or distant recurrence or mortality. Longer-term follow-up is needed to verify that this remains true with time.
Figures
References
-
- Lyman GH, Giuliano AE, Somerfield MR, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology guideline recommendations for sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:7703–20. - PubMed
-
- Cserni G, Gregori D, Merletti F, et al. Meta-analysis of non-sentinel node metastases associated with micrometastatic sentinel nodes in breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2004;91:1245–52. - PubMed
-
- Van Zee KJ, Manasseh DME, Bevilacqua JLB, et al. A nomogram for predicting the likelihood of additional nodal metastases in breast cancer patients with a positive sentinel node biopsy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2003;10:1140–51. - PubMed
-
- Reed J, Rosman M, Verbanac KM, Mannie A, Cheng Z, Tafra L. Prognostic implications of isolated tumor cells and micrometastases in sentinel nodes of patients with invasive breast cancer: 10-year analysis of patients enrolled in the prospective East Carolina University/Anne Arundel Medical Center sentinel node multicenter study. J Am Coll Surg. 2009;208:333–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

