A eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein promotes mRNA decapping and is required for PUF repression
- PMID: 22890846
- PMCID: PMC3457345
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00483-12
A eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein promotes mRNA decapping and is required for PUF repression
Abstract
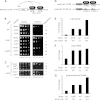
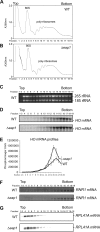
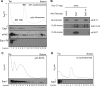
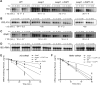
PUF proteins are eukaryotic RNA-binding proteins that repress specific mRNAs. The mechanisms and corepressors involved in PUF repression remain to be fully identified. Here, we investigated the mode of repression by Saccharomyces cerevisiae Puf5p and Puf4p and found that Puf5p specifically requires Eap1p to repress mRNAs, whereas Puf4p does not. Surprisingly, we observed that Eap1p, which is a member of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E)-binding protein (4E-BP) class of translational inhibitors, does not inhibit the efficient polyribosome association of a Puf5p target mRNA. Rather, we found that Eap1p accelerates mRNA degradation by promoting decapping, and the ability of Eap1p to interact with eIF4E facilitates this activity. Deletion of EAP1 dramatically reduces decapping, resulting in accumulation of deadenylated, capped mRNA. In support of this phenotype, Eap1p associates both with Puf5p and the Dhh1p decapping factor. Furthermore, recruitment of Eap1p to downregulated mRNA is mediated by Puf5p. On the basis of these results, we propose that Puf5p promotes decapping by recruiting Eap1p and associated decapping factors to mRNAs. The implication of these findings is that a 4E-BP can repress protein expression by promoting specific mRNA degradation steps in addition to or in lieu of inhibiting translation initiation.
Figures
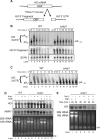
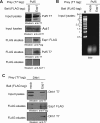
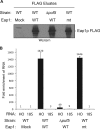
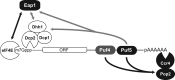
References
-
- Asaoka-Taguchi M, Yamada M, Nakamura A, Hanyu K, Kobayashi S. 1999. Maternal Pumilio acts together with Nanos in germline development in Drosophila embryos. Nat. Cell Biol. 1:431–437 - PubMed
-
- Beelman CA, et al. 1996. An essential component of the decapping enzyme required for normal rates of mRNA turnover. Nature 382:642–646 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
