Biochemical studies on sphingolipids of Artemia franciscana: complex neutral glycosphingolipids
- PMID: 22890904
- PMCID: PMC3606520
- DOI: 10.1007/s10719-012-9436-8
Biochemical studies on sphingolipids of Artemia franciscana: complex neutral glycosphingolipids
Abstract
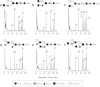
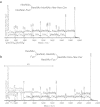
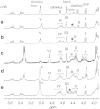
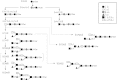
Brine shrimp are primitive crustacean arthropodal model organisms, second to daphnia, which can survive in high-salinity environments. Their oviposited cysts, cuticle-covered diapausing eggs, are highly resistant to dryness. To elucidate specialties of brine shrimp, this study characterized glycosphingolipids, which are signal transduction-associated material. A group of novel and complex fucosyl glycosphingolipids were separated and identified from cysts of the brine shrimp Artemia franciscana by repeated lipid extraction, alkaline methanolysis, acid treatment, successive column chromatography, and post-source decay measurements by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Structures of the glycosphingolipids were elucidated by conventional structural characterization and mass spectrometry, and the compounds were identified as GlcNAcβ1-3GalNAcβ1-4(GlcNAcα1-2Fucα1-3)GlcNAcβ1-3Manβ1-4Glcβ1-Cer, GalNAcβ1-4(Fucα1-3)GlcNAcβ1-3GalNAcβ1-4(GlcNAcα1-2Fucα1-3)GlcNAcβ1-3Manβ1-4Glcβ1-Cer, and GalNAcβ1-4(GlcNAcα1-2Fucα1-3)GlcNAcβ1-3GalNAcβ1-4(GlcNAcα1-2Fucα1-3)GlcNAcβ1-3Manβ1-4Glcβ1-Cer. These compounds also contained a branching, non-arthro-series disaccharide with an α-GlcNAc terminus, similar to that found in a previously reported ceramide hexasaccharide (III(3)(GlcNAcα2Fucα)-At4Cer). The glycans within these complex GSLs are longer than reported glycans of the animal kingdom containing α-GlcNAc terminus. These complex GSLs as well as the longest GSL with ten sugar residues, ceramide decasaccharide (CDeS), contain the fucosylated LacdiNAc sequence reported to associate with parasitism/immunosuppression and the α-GlcNAc terminus reported to show a certain antibacterial effect in other reports. CDeS, the longest GSL of this species, was found in the highest amount, which indicates that CDeS may be functionally important.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Biochemical studies on sphingolipids of Artemia franciscana: novel neutral glycosphingolipids.J Lipid Res. 2011 Feb;52(2):308-17. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M010173. Epub 2010 Nov 9. J Lipid Res. 2011. PMID: 21062954 Free PMC article.
-
A novel fucosyl glycosphingolipid of brine shrimp that is highly sensitive to endoglycoceramidase.Glycobiology. 2009 Dec;19(12):1446-51. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwp118. Epub 2009 Aug 21. Glycobiology. 2009. PMID: 19700487
-
Structural characterization of neutral glycosphingolipids by thin-layer chromatography coupled to matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization quadrupole ion trap time-of-flight MS/MS.Anal Chem. 2006 Aug 15;78(16):5736-43. doi: 10.1021/ac0605501. Anal Chem. 2006. PMID: 16906718
-
Insect glycolipids.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jan 24;1123(2):117-26. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90101-z. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992. PMID: 1739742 Review.
-
Glycosphingolipid structural analysis and glycosphingolipidomics.Methods Enzymol. 2005;405:300-69. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)05012-3. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 16413319 Review.
Cited by
-
The Structural Diversity of Natural Glycosphingolipids (GSLs).J Carbohydr Chem. 2022;41(2-3):63-154. doi: 10.1080/07328303.2022.2063308. Epub 2022 May 26. J Carbohydr Chem. 2022. PMID: 36561362 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomics and the origin of obligate parthenogenesis.Heredity (Edinb). 2023 Aug;131(2):119-129. doi: 10.1038/s41437-023-00628-3. Epub 2023 Jun 6. Heredity (Edinb). 2023. PMID: 37280308 Free PMC article.
-
Gene transcription, metabolite and lipid profiling in eco-indicator daphnia magna indicate diverse mechanisms of toxicity by legacy and emerging flame-retardants.Environ Sci Technol. 2015 Jun 16;49(12):7400-10. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b00977. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Environ Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 25985095 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Profile Changes During the Development of Artemia franciscana, From Cysts to the First Two Naupliar Stages.Front Physiol. 2019 Jan 22;9:1872. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01872. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30723418 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Gastric Cancer Biomarkers Using 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometry.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 9;11(9):e0162222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162222. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27611679 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yu RK, Yanagisawa M, Ariga T. Glycosphingolipid structures. In: Kamerling JP, editor. Comprehensive Glycoscience from Chemistry to Systems Biology1: Introduction to Glycoscience; Synthesis of Carbohydrates. Oxford: Elsevier; 2007. pp. 73–122.
-
- Itonori S, Sugita M. Glycophylogenetic aspects of lower animals. In: Kamerling JP, editor. Comprehensive Glycoscience from Chemistry to Systems Biology 3: Biochemistry of Glycoconjugate Glycans; Carbohydrate-Mediated Interactions. Oxford: Elsevier; 2007. pp. 253–284.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

