White paper: recommendations on the conduct of superiority and organism-specific clinical trials of antibacterial agents for the treatment of infections caused by drug-resistant bacterial pathogens
- PMID: 22891041
- PMCID: PMC3657525
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/cis688
White paper: recommendations on the conduct of superiority and organism-specific clinical trials of antibacterial agents for the treatment of infections caused by drug-resistant bacterial pathogens
Abstract
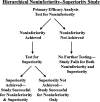
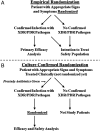
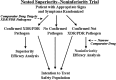
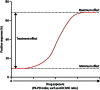
There is a critical need for new pathways to develop antibacterial agents to treat life-threatening infections caused by highly resistant bacteria. Traditionally, antibacterial agents have been studied in noninferiority clinical trials that focus on one site of infection (eg, pneumonia, intra-abdominal infection). Conduct of superiority trials for infections caused by highly antibiotic-resistant bacteria represents a new, and as yet, untested paradigm for antibacterial drug development. We sought to define feasible trial designs of antibacterial agents that could enable conduct of superiority and organism-specific clinical trials. These recommendations are the results of several years of active dialogue among the white paper's drafters as well as external collaborators and regulatory officials. Our goal is to facilitate conduct of new types of antibacterial clinical trials to enable development and ultimately approval of critically needed new antibacterial agents.
Figures

References
-
- Falagas ME, Bliziotis IA. Pandrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria: the dawn of the post-antibiotic era? Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2007;29:630–6. - PubMed
-
- Falagas ME, Rafailidis PI, Matthaiou DK, Virtzili S, Nikita D, Michalopoulos A. Pandrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii infections: characteristics and outcome in a series of 28 patients. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2008;32:450–4. - PubMed
-
- Valencia R, Arroyo LA, Conde M, et al. Nosocomial outbreak of infection with pan-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a tertiary care university hospital. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2009;30:257–63. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann MS, Eber MR, Laxminarayan R. Increasing resistance of Acinetobacter species to imipenem in United States hospitals, 1999–2006. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2010;31:196–7. - PubMed

