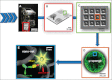
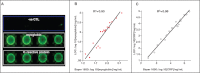
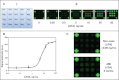
Programmable bio-nanochip technology for the diagnosis of cardiovascular disease at the point-of-care
- PMID: 22891104
- PMCID: PMC3405784
- DOI: 10.14797/mdcj-8-1-6
Programmable bio-nanochip technology for the diagnosis of cardiovascular disease at the point-of-care
Erratum in
- Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2012 Jul-Sep;8(3):48
Abstract
Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of death in the world and continues to serve as the major contributor to healthcare costs. Likewise, there is an ever-increasing need and demand for novel and more efficient diagnostic tools for the early detection of cardiovascular disease, especially at the point-of-care (POC). This article reviews the programmable bio-nanochip (P-BNC) system, a new medical microdevice approach with the capacity to deliver both high performance and reduced cost. This fully integrated, total analysis system leverages microelectronic components, microfabrication techniques, and nanotechnology to noninvasively measure multiple cardiac biomarkers in complex fluids, such as saliva, while offering diagnostic accuracy equal to laboratory-confined reference methods. This article profiles the P-BNC approach, describes its performance in real-world testing of clinical samples, and summarizes new opportunities for medical microdevices in the field of cardiac diagnostics.
Keywords: P-BNC; bio-nanochips; cardiac biomarkers; cardiovascular disease; in vitro diagnostics; lab-on-a-chip technologies; point of care testing; programmable bio-nanochips.
Figures
References
-
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Friday G, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics — 2007 Update, A Report From the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2007 Feb 6;115(5):e69–e171.. Epub 2006 Dec 28. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Flegal K, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics — 2009 Update, A Report From the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2009;119(3):e21–181.. Epub 2008 Dec 15. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, De Simone G, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics — 2010 update, A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;121:e46–e215.. Epub 2009 Dec 17. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization [Internet] Geneva Switzerland: World Health Organization; c2011. Programmes and projects: Global atlas on cardiovascular disease prevention and control; 2011 Sep 19 [cited 2011 Nov 21]. Available from: http://www.who.int/cardiovascular_diseases/en/
-
- Budoff MJ, Achenbach S, Duerinckx A. Clinical utility of computed tomography and magnetic resonance techniques for noninvasive coronary angiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42:1867–78.. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous