High-resolution CT vascular imaging using blood pool contrast agents
- PMID: 22891106
- PMCID: PMC3405778
- DOI: 10.14797/mdcj-8-1-18
High-resolution CT vascular imaging using blood pool contrast agents
Abstract
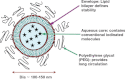
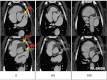
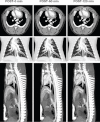
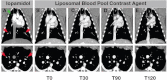
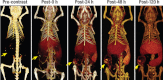
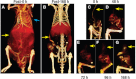
While the evolution of computed tomography imaging in the last 2 decades has been driven almost exclusively by improvements in the instrumentation and processing algorithms, there have been comparatively modest advances in contrast agent technology.A notable change in the last decade has been the development of blood pool contrast agents based on nanoparticle technology.While not yet ready for clinical use, the stable and uniform opacification provided by these agents in normal vasculature and controlled extravasation in compromised vasculature enables novel techniques for imaging and diagnosis of pathologies. This manuscript presents preclinical examples demonstrating cardiovascular pathologies and tumor characterization by high-resolution computed tomography imaging.
Keywords: CT; blood pool; computed tomography; contrast agent; liposome; tumor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High-resolution 3D visualization of nanomedicine distribution in tumors.Theranostics. 2020 Jan 1;10(2):880-897. doi: 10.7150/thno.37178. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 31903157 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle contrast agents for computed tomography: a focus on micelles.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2014 Jan-Feb;9(1):37-52. doi: 10.1002/cmmi.1551. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24470293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in nanoparticle imaging technology for vascular pathologies.Annu Rev Med. 2015;66:177-93. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-042513-125551. Annu Rev Med. 2015. PMID: 25587649 Review.
-
Design of nanovectors for therapy and imaging of cardiovascular diseases.Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2012 Jan;8(1):13-7. doi: 10.14797/mdcj-8-1-13. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2012. PMID: 22891105 Free PMC article.
-
Colloidal gold nanoparticles as a blood-pool contrast agent for X-ray computed tomography in mice.Invest Radiol. 2007 Dec;42(12):797-806. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e31811ecdcd. Invest Radiol. 2007. PMID: 18007151
Cited by
-
Feasibility of multi-contrast imaging on dual-source photon counting detector (PCD) CT: An initial phantom study.Med Phys. 2019 Sep;46(9):4105-4115. doi: 10.1002/mp.13668. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 31215659 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Quantitative Microcomputed Tomographic Analysis of Vasculature and Organs in a Normal and Diseased Mouse Model.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 24;11(2):e0150085. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150085. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26910759 Free PMC article.
-
Computed Tomography Imaging of Solid Tumors Using a Liposomal-Iodine Contrast Agent in Companion Dogs with Naturally Occurring Cancer.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 31;11(3):e0152718. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152718. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27031614 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo small animal micro-CT using nanoparticle contrast agents.Front Pharmacol. 2015 Nov 4;6:256. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00256. eCollection 2015. Front Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26581654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in micro-CT imaging of small animals.Phys Med. 2021 Aug;88:175-192. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2021.07.005. Epub 2021 Jul 17. Phys Med. 2021. PMID: 34284331 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Petersilka M, Bruder H, Krauss B, Stierstorfer K, Flohr TG. Technical principles of dual source CT. Eur J Radiol. 2008 Dec;68(3):362–8.. - PubMed
-
- Gupta R, Cheung AC, Bartling SH, Lisauskas J, Grasruck M, Leidecker C, et al. Flat-panel volume CT: fundamental principles, technology, and applications. Radiographics. 2008 Nov-Dec;28(7):2009–22.. - PubMed
-
- Eide KR, Ødegård A, Myhre HO, Lydersen S, Hatlinghus S, Haraldseth O. DynaCT during EVAR — a comparison with multidetector CT. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2009 Jan;37(1):23–30.. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical