Efficacy of memoral herbal on prevention of electroconvulsive therapy-induced memory impairment in mood disorder patients (isfahan - iran 2011)
- PMID: 22891152
- PMCID: PMC3415191
Efficacy of memoral herbal on prevention of electroconvulsive therapy-induced memory impairment in mood disorder patients (isfahan - iran 2011)
Abstract
Background: Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is one of the most efficacious treatment for major depressive disorder (MDD), it is also used as a rapid and efficacious treatment for other psychiatric disorders, especially treatment resistant ones. The cognitive impairment is one of the most important side effects of ECT. This study examined the Memoral herbal efficacy in prevention of ECT-induced memory impairment.
Methods: In a randomized clinical trial, 70 patients with mood disorders who were candidates for ECT enrolled in either Memoral or Control group, and received either Memoral or placebo. The memory was assessed by Addenbrook Cognitive Examination (ACE), and the findings were analyzed by ANOVA under SPSS18.
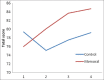
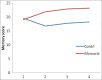
Results: The Memoral group patients showed significantly higher total ACE scores than placebo group (P < 0.001). The scores of attention and orientation, verbal fluency and memory subscales not only never decreased during the study in Memoral group, but also increased. There was no significant difference between these scores of Memoral and placebo groups for the subscales of language and visuospacial ability.
Conclusion: The Memoral herbal is an efficacious and safe choice in prevention of ECT- induced cognitive impairment.
Keywords: Cognitive impairment; ECT; Memoral herbal; memory.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of desmopressin (DDAVP) on memory impairment following electroconvulsive therapy (ECT).Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2004 Jun;16(3):130-7. doi: 10.1111/j.0924-2708.2004.00064.x. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2004. PMID: 26984164
-
Preventive effect of liothyronine on electroconvulsive therapy-induced memory deficit in patients with major depressive disorder: a double-blind controlled clinical trial.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:503918. doi: 10.1155/2015/503918. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25945337 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Concomitant Anticonvulsants With Bitemporal Electroconvulsive Therapy: A Randomized Controlled Trial With Clinical and Neurobiological Application.J ECT. 2017 Mar;33(1):16-21. doi: 10.1097/YCT.0000000000000357. J ECT. 2017. PMID: 27668943 Clinical Trial.
-
Neurocognitive effects after brief pulse and ultrabrief pulse unilateral electroconvulsive therapy for major depression: a review.J Affect Disord. 2012 Nov;140(3):233-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2012.02.024. Epub 2012 May 15. J Affect Disord. 2012. PMID: 22595374 Review.
-
The Neurobiological Basis of Cognitive Side Effects of Electroconvulsive Therapy: A Systematic Review.Brain Sci. 2021 Sep 26;11(10):1273. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11101273. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34679338 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological interventions to diminish cognitive side effects of electroconvulsive therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2022 Apr;145(4):343-356. doi: 10.1111/acps.13397. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2022. PMID: 35075641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sadock BJ, Sadock VA. Kaplan and Sadock's Synopsis of psychiatry. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2007. pp. 1117–24.
-
- Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, Ruiz P. Kaplan and Sadock's, Comprehensive Textbook of psychiatry. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2009. pp. 3285–300.
-
- Rao NP, Palaniyappan P, Chandur J, Venkatasubramanian G, Gangadhar BN. Successful use of donepezil in treatment of cognitive impairment caused by maintenance electroconvulsive therapy: A case report. J ECT. 2009;25:216–8. - PubMed
-
- Matthews JD, Blais M, Park L, Welch C, Baity M, Murakami J, et al. The impact of galantamine on cognition and mood during electroconvulsive therapy: A pilot study. J Psychiatr Res. 2008;42:526–31. - PubMed
-
- Andrade C, Shaikh SA, Narayan L, Blasey C, Belanoff J. Administration of a selective glucocorticoid antagonist attenuates electroconvulsive shock-induced retrograde amnesia. J Neural Transm. 2012;119:337–44. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
