Nuclear factor-κB binding motifs specify Toll-like receptor-induced gene repression through an inducible repressosome
- PMID: 22891325
- PMCID: PMC3435186
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1119842109
Nuclear factor-κB binding motifs specify Toll-like receptor-induced gene repression through an inducible repressosome
Abstract
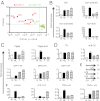
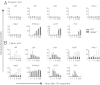
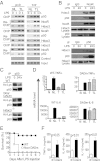
Sustained Toll-like receptor (TLR) stimulation continuously activates antimicrobial genes but paradoxically represses inflammatory genes. This phenomenon, termed TLR tolerance, is essential for preventing fatal inflammatory conditions such as sepsis, but its underlying mechanisms are unclear. We report here that NF-κB binding nucleic acids of gene promoters are tolerogenic motifs, which selectively recruit an NcoR-Hdac3-deacetylated-p50 repressosome to inflammatory genes. Genome-wide analyses of TLR4-induced genes revealed that NF-κB motifs were the only regulatory elements significantly enriched in tolerizable genes. Mutating the NF-κB motifs of tolerizable genes converted them into nontolerizable ones, whereas inserting NF-κB binding motifs into nontolerizable genes conferred the tolerance. Although NF-κB p50 was essential for assembling the repressosome, genetic disruption of the NcoR-Hdac3 interaction alone was sufficient to completely abolish TLR4 tolerance and to render mice vulnerable to sepsis. Thus, the specificity of TLR tolerance is dictated by evolutionally conserved nucleic acid motifs that bound by NF-κB and the NcoR repressosome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Induction of in vitro reprogramming by Toll-like receptor (TLR)2 and TLR4 agonists in murine macrophages: effects of TLR "homotolerance" versus "heterotolerance" on NF-kappa B signaling pathway components.J Immunol. 2003 Jan 1;170(1):508-19. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.1.508. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12496438
-
MyD88 adapter-like (Mal)/TIRAP interaction with TRAF6 is critical for TLR2- and TLR4-mediated NF-kappaB proinflammatory responses.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 4;284(36):24192-203. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.023044. Epub 2009 Jul 10. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19592497 Free PMC article.
-
Runt-related Transcription Factor 1 (RUNX1) Binds to p50 in Macrophages and Enhances TLR4-triggered Inflammation and Septic Shock.J Biol Chem. 2016 Oct 14;291(42):22011-22020. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.715953. Epub 2016 Aug 29. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27573239 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitination of ECSIT is crucial for the activation of p65/p50 NF-κBs in Toll-like receptor 4 signaling.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Jan 1;26(1):151-60. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-08-1277. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25355951 Free PMC article.
-
Pellino-3 promotes endotoxin tolerance and acts as a negative regulator of TLR2 and TLR4 signaling.J Leukoc Biol. 2015 Dec;98(6):963-74. doi: 10.1189/jlb.2VMA0515-229RR. Epub 2015 Aug 26. J Leukoc Biol. 2015. PMID: 26310831 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nuclear receptors in inflammation control: repression by GR and beyond.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Nov 5;380(1-2):55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.04.006. Epub 2013 Apr 26. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23623868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Myeloid Cells.Microbiol Spectr. 2016 Jun;4(3):10.1128/microbiolspec.MCHD-0010-2015. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MCHD-0010-2015. Microbiol Spectr. 2016. PMID: 27337441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative regulatory approaches to the attenuation of Toll-like receptor signaling.Exp Mol Med. 2013 Feb 22;45(2):e11. doi: 10.1038/emm.2013.28. Exp Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23429360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of macrophages: from homeostasis maintenance to host defense.Cell Mol Immunol. 2020 Jan;17(1):36-49. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0315-0. Epub 2019 Oct 29. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31664225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of transcription by B cell Leukemia 3 (Bcl-3) protein requires interaction with nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) p50.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 7;289(10):7059-7067. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.551986. Epub 2014 Jan 23. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24459141 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Foster SL, Hargreaves DC, Medzhitov R. Gene-specific control of inflammation by TLR-induced chromatin modifications. Nature. 2007;447:972–978. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto M, et al. Regulation of Toll/IL-1-receptor-mediated gene expression by the inducible nuclear protein IkappaBzeta. Nature. 2004;430:218–222. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:816–825. - PubMed
-
- Broad A, Jones DE, Kirby JA. Toll-like receptor (TLR) response tolerance: A key physiological “damage limitation” effect and an important potential opportunity for therapy. Curr Med Chem. 2006;13:2487–2502. - PubMed
-
- Biswas SK, Lopez-Collazo E. Endotoxin tolerance: New mechanisms, molecules and clinical significance. Trends Immunol. 2009;30:475–487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

