The development of a GeXP-based multiplex reverse transcription-PCR assay for simultaneous detection of sixteen human respiratory virus types/subtypes
- PMID: 22891685
- PMCID: PMC3462154
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-12-189
The development of a GeXP-based multiplex reverse transcription-PCR assay for simultaneous detection of sixteen human respiratory virus types/subtypes
Abstract
Background: Existing standard non-molecular diagnostic methods such as viral culture and immunofluorescent (DFA) are time-consuming, labor intensive or limited sensitivity. Several multiplex molecular assays are costly. Therefore, there is a need for the development of a rapid and sensitive diagnosis of respiratory viral pathogens.
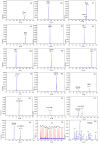
Methods: A GeXP-based multiplex RT-PCR assay (GeXP assay) was developed to detect simultaneously sixteen different respiratory virus types/subtypes. Seventeen sets of chimeric primers were used to initiate the RT-PCR, and one pair of universal primers was used for the subsequent cycles of the RT-PCR. The specificity of the GeXP assay was examined with positive controls for each virus type/subtype. The sensitivity was evaluated by performing the assay on serial ten-fold dilutions of in vitro-transcribed RNA of all RNA viruses and the plasmids containing the Adv and HBoV target sequence. GeXP assay was further evaluated using 126 clinical specimens and compared with Luminex xTAG RVP Fast assay.
Results: The GeXP assay achieved a sensitivity of 20-200 copies for a single virus and 1000 copies when all of the 16 pre-mixed viral targets were present. Analyses of 126 clinical specimens using the GeXP assay demonstrated that GeXP assay and the RVP Fast assay were in complete agreement for 109/126 (88.51%) of the specimens. GeXP assay was more sensitive than the RVP Fast assay for the detection of HRV and PIV3, and slightly less sensitive for the detection of HMPV, Adv, RSVB and HBoV. The whole process of the GeXP assay for the detection of 12 samples was completed within 2.5 hours.
Conclusions: In conclusion, the GeXP assay is a rapid, cost-effective, sensitive, specific and high throughput method for the detection of respiratory virus infections.
Figures
References
-
- Cant AJ, Gordon SB, Read RC, Hart CA, Winstanley C. Respiratory infections. J Med Microbiol. 2002;51(11):903–914. - PubMed
-
- Mahony J, Chong S, Merante F, Yaghoubian S, Sinha T, Lisle C, Janeczko R. Development of a respiratory virus panel test for detection of twenty human respiratory viruses by use of multiplex PCR and a fluid microbead-based assay. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45(9):2965–2970. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02436-06. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Henrickson KJ. Advances in the laboratory diagnosis of viral respiratory disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004;23(1 Suppl):S6–S10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

