Nm23/nucleoside diphosphate kinase-A as a potent prognostic marker in invasive pancreatic ductal carcinoma identified by proteomic analysis of laser micro-dissected formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue
- PMID: 22892044
- PMCID: PMC3582529
- DOI: 10.1186/1559-0275-9-8
Nm23/nucleoside diphosphate kinase-A as a potent prognostic marker in invasive pancreatic ductal carcinoma identified by proteomic analysis of laser micro-dissected formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic cancer is among the most lethal malignancies worldwide. This study aimed to identify a novel prognostic biomarker, facilitating treatment selection, using mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomic analysis with formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue.
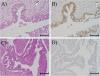
Results: The two groups with poor prognosis (n = 4) and with better prognosis (n = 4) had been carefully chosen among 96 resected cases of pancreatic cancer during 1998 to 2007 in Tohoku University Hospital. Although those 2 groups had adjusted background (UICC-Stage IIB, Grade2, R0, gemcitabine adjuvant), there was a significant difference in postoperative mean survival time (poor 21.0 months, better 58.1 months, P = 0.0067). Cancerous epithelial cells collected from FFPE tissue sections by laser micro-dissection (LMD) were processed for liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). In total, 1099 unique proteins were identified and 6 proteins showed different expressions in the 2 groups by semi-quantitative comparison. Among these 6 proteins, we focused on Nm23/Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase A (NDPK-A) and immunohistochemically confirmed its expression in the cohort of 96 cases. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed high Nm23/NDPK-A expression to correlate with significantly worse overall survival (P = 0.0103). Moreover, in the multivariate Cox regression model, Nm23/NDPK-A over-expression remained an independent predictor of poor survival with a hazard ratio of 1.97 (95% CI 1.16-3.56, P = 0.0110).
Conclusions: We identified 6 candidate prognostic markers for postoperative pancreatic cancer using FFPE tissues and immunohistochemically demonstrated high Nm23/NDPK-A expression to be a useful prognostic marker for pancreatic cancer.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Novel prognostic protein markers of resectable pancreatic cancer identified by coupled shotgun and targeted proteomics using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues.Int J Cancer. 2013 Mar 15;132(6):1368-82. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27797. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 22915188
-
Nm23 protein expression in ductal in situ and invasive human breast carcinoma.J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 May 5;85(9):727-31. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.9.727. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993. PMID: 8386774
-
[The regulation of nm23-H1/NDPK-A in different processes of regional lymph node metastases of oral squamous cell carcinomas].Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2003 Aug;21(4):263-6. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 14513578 Chinese.
-
c-erbB-2, p53, and nm23 proteins as prognostic factors in patients with epithelial ovarian carcinoma.Croat Med J. 2003 Aug;44(4):429-34. Croat Med J. 2003. PMID: 12950146
-
Prognostic significance of Nm23/NDPK expression in breast carcinoma, assessed on 10-year follow-up by automated and quantitative immunocytochemical assays.J Pathol. 1998 Apr;184(4):401-7. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199804)184:4<401::AID-PATH1220>3.0.CO;2-U. J Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9664906
Cited by
-
Prognostic Value of NME1 (NM23-H1) in Patients with Digestive System Neoplasms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 12;11(8):e0160547. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160547. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27518571 Free PMC article.
-
An Integrated Meta-Analysis of Secretome and Proteome Identify Potential Biomarkers of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Mar 18;12(3):716. doi: 10.3390/cancers12030716. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32197468 Free PMC article.
-
PharmGKB summary: gemcitabine pathway.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2014 Nov;24(11):564-74. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0000000000000086. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25162786 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Blocking eIF5A modification in cervical cancer cells alters the expression of cancer-related genes and suppresses cell proliferation.Cancer Res. 2014 Jan 15;74(2):552-62. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0474. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24220243 Free PMC article.
-
Novel biomarkers distinguishing pancreatic head Cancer from distal cholangiocarcinoma based on proteomic analysis.BMC Cancer. 2019 Apr 5;19(1):318. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5548-x. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30953499 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
