The involvement of the wnt signaling pathway and TCF7L2 in diabetes mellitus: The current understanding, dispute, and perspective
- PMID: 22892353
- PMCID: PMC3468386
- DOI: 10.1186/2045-3701-2-28
The involvement of the wnt signaling pathway and TCF7L2 in diabetes mellitus: The current understanding, dispute, and perspective
Abstract
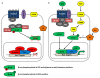
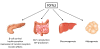
The Wnt signaling pathway was initially discovered for its role in tumorigenesis and the development of Drosophila and other eukaryotic organisms. The key effector of this pathway, the bipartite transcription factor β-cat/TCF, is formed by free β-catenin (β-cat) and a TCF protein, including TCF7L2. Extensive recent investigations have highlighted the role of the Wnt signaling pathway in metabolic homeostasis and its implication in diabetes and other metabolic diseases. Genome-wide association studies have shown that several key components of the Wnt signaling pathway are implicated in metabolic homeostasis and the development of type 2 diabetes (T2D). Despite controversial observations regarding the role of Wnt signaling in the development and function of pancreatic islets, the discovery of the association between certain single nucleotide polymorphisms of TCF7L2 and T2D susceptibility has fueled great efforts to explore the role of Wnt signaling in the function of pancreatic β-cells and glucose homeostasis. Here we have introduced our basic understanding of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway, summarized our current knowledge on its implication in metabolic homeostasis and T2D, discussed the work on TCF7L2 as a T2D susceptibility gene, and presented the controversial role of Wnt signaling and TCF7L2 in pancreatic islets as well as their potential metabolic function in other organs. We then expanded our view into the crosstalk among Wnt, insulin and FOXO signaling cascades, which further illustrates the complexity of the Wnt signaling pathway in metabolic homeostasis. Finally, we have presented our perspectives.
Figures


References
-
- Yi F, Brubaker PL, Jin T. TCF-4 mediates cell type-specific regulation of proglucagon gene expression by beta-catenin and glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:1457–1464. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

