BCAR4 induces antioestrogen resistance but sensitises breast cancer to lapatinib
- PMID: 22892392
- PMCID: PMC3464772
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.351
BCAR4 induces antioestrogen resistance but sensitises breast cancer to lapatinib
Abstract
Background: High BCAR4 and ERBB2 mRNA levels in primary breast cancer associate with tamoxifen resistance and poor patient outcome. We determined whether BCAR4 expression sensitises breast cancer cells to lapatinib, and identifies a subgroup of patients who possibly may benefit from ERBB2-targeted therapies despite having tumours with low ERBB2 expression.
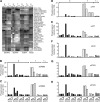
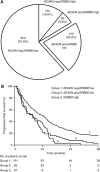
Methods: Proliferation assays were applied to determine the effect of BCAR4 expression on lapatinib treatment. Changes in cell signalling were quantified with reverse-phase protein microarrays. Quantitative reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) of ERBB2 and BCAR4 was performed in 1418 primary breast cancers. Combined BCAR4 and ERBB2 mRNA levels were evaluated for association with progression-free survival (PFS) in 293 oestrogen receptor-α (ER)-positive patients receiving tamoxifen as first-line monotherapy for recurrent disease.
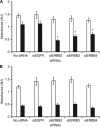
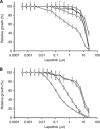
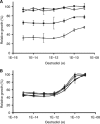
Results: BCAR4 expression strongly sensitised ZR-75-1 and MCF7 breast cancer cells to the combination of lapatinib and antioestrogens. Lapatinib interfered with phosphorylation of ERBB2 and its downstream mediators AKT, FAK, SHC, STAT5, and STAT6. Reverse transcriptase-PCR analysis showed that 27.6% of the breast cancers were positive for BCAR4 and 22% expressed also low levels of ERBB2. The clinical significance of combining BCAR4 and ERBB2 mRNA status was underscored by the finding that the group of patients having BCAR4-positive/ERBB2-low-expressing cancers had a shorter PFS on tamoxifen treatment than the BCAR4-negative group.
Conclusion: This study shows that BCAR4 expression identifies a subgroup of ER-positive breast cancer patients without overexpression of ERBB2 who have a poor outcome and might benefit from combined ERBB2-targeted and antioestrogen therapy.
© 2012 Cancer Research UK
Conflict of interest statement
JDW: ownership interest and paid consultant for Theranostics Health, LLC. EFP: ownership interest, member of advisory board and unpaid consultant for Theranostics Health, LLC. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relevance of BCAR4 in tamoxifen resistance and tumour aggressiveness of human breast cancer.Br J Cancer. 2010 Oct 12;103(8):1284-91. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605884. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Br J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20859285 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of BCAR4, a novel oncogene causing endocrine resistance in human breast cancer cells.J Cell Physiol. 2011 Jul;226(7):1741-9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22503. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21506106
-
Breast Cancer Anti-Estrogen Resistance 4 (BCAR4) Drives Proliferation of IPH-926 lobular Carcinoma Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 28;10(8):e0136845. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136845. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26317614 Free PMC article.
-
Acquired resistance to small molecule ErbB2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Nov 1;14(21):6730-4. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0581. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18980964 Review.
-
Mechanisms of lapatinib resistance in HER2-driven breast cancer.Cancer Treat Rev. 2015 Dec;41(10):877-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2015.08.001. Epub 2015 Aug 8. Cancer Treat Rev. 2015. PMID: 26276735 Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting lncRNA-disease associations and constructing lncRNA functional similarity network based on the information of miRNA.Sci Rep. 2015 Aug 17;5:13186. doi: 10.1038/srep13186. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26278472 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA-disease association prediction based on matrix decomposition of elastic network and collaborative filtering.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 26;12(1):12700. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16594-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35882886 Free PMC article.
-
BCAR4 Expression as a Predictive Biomarker for Endocrine Therapy Resistance in Breast Cancer.Clin Breast Cancer. 2024 Jun;24(4):368-375.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2024.02.007. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Clin Breast Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38443227 Free PMC article.
-
The role of long non-coding RNA BCAR4 in human cancers.Hum Cell. 2021 Sep;34(5):1301-1309. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00556-6. Epub 2021 May 27. Hum Cell. 2021. PMID: 34041673 Review.
-
LncRNA RUSC1-AS1 promotes osteosarcoma progression through regulating the miR-340-5p and PI3K/AKT pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 May 28;13(16):20116-20130. doi: 10.18632/aging.203047. Epub 2021 May 28. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34048366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bates NP, Hurst HC (1997) An intron 1 enhancer element mediates oestrogen-induced suppression of ERBB2 expression. Oncogene 15(4): 473–481 - PubMed
-
- Brinkman A, Van der Flier S, Kok EM, Dorssers LCJ (2000) BCAR1, a human homologue of the adapter protein p130Cas and ntiestrogen resistance in breast cancer cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 92: 112–120 - PubMed
-
- Burris HA, Hurwitz HI, Dees EC, Dowlati A, Blackwell KL, O'Neil B, Marcom PK, Ellis MJ, Overmoyer B, Jones SF, Harris JL, Smith DA, Koch KM, Stead A, Mangum S, Spector NL (2005) Phase I safety, pharmacokinetics, and clinical activity study of lapatinib (GW572016), a reversible dual inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic carcinomas. J Clin Oncol 23(23): 5305–5313 - PubMed
-
- Carraway KL, Price-Schiavi SA, Komatsu M, Jepson S, Perez A, Carraway CA (2001) Muc4/sialomucin complex in the mammary gland and breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 6(3): 323–337 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

