Dynamic changes in DNA methylation of stress-associated genes (OXTR, BDNF ) after acute psychosocial stress
- PMID: 22892716
- PMCID: PMC3432191
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2012.77
Dynamic changes in DNA methylation of stress-associated genes (OXTR, BDNF ) after acute psychosocial stress
Abstract
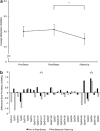
Environmentally induced epigenetic alterations are related to mental health. We investigated quantitative DNA methylation status before and after an acute psychosocial stressor in two stress-related genes: oxytocin receptor (OXTR) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF ). The cross sectional study took place at the Division of Theoretical and Clinical Psychobiology, University of Trier, Germany and was conducted from February to August 2009. We included 83 participants aged 61-67 years. Thereof, 76 participants completed the full study procedure consisting of blood sampling before (pre-stress), 10 min after (post-stress) and 90 min after (follow-up) the Trier social stress test. We assessed quantitative DNA methylation of whole-blood cells using Sequenom EpiTYPER. Methylation status differed between sampling times in one target sequence of OXTR (P<0.001): methylation increased from pre- to post-stress (P=0.009) and decreased from post-stress to follow-up (P<0.001). This decrease was also found in a second target sequence of OXTR (P=0.034), where it lost statistical significance when blood cell count was statistically controlled. We did not detect any time-associated differences in methylation status of the examined BDNF region. The results suggest a dynamic regulation of DNA methylation in OXTR-which may in part reflect changes in blood cell composition-but not BDNF after acute psychosocial stress. This may enhance the understanding of how psychosocial events alter DNA methylation and could provide new insights into the etiology of mental disorders.
Figures


References
-
- Docherty S, Mill J. Epigenetic mechanisms as mediators of environmental risks for psychiatric disorders. Psychiatry. 2008;7:500–506.
-
- National Institute of Mental Health. National Institute of Mental Health Strategic Plan. 2008.
-
- Scarano MI, Strazzullo M, Matarazzo MR, D'Esposito M. DNA methylation 40 years later: Its role in human health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2005;204:21–35. - PubMed
-
- Fuchikami M, Morinobu S, Segawa M, Yamawaki S. DNA methylation profiles of the BDNF gene in patients with major depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010;13:147.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

