Polyglutamine (polyQ) disorders: the chromatin connection
- PMID: 22892726
- PMCID: PMC3474664
- DOI: 10.4161/nucl.21481
Polyglutamine (polyQ) disorders: the chromatin connection
Abstract
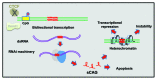
Polyglutamine (PolyQ)-related diseases are dominant late-onset genetic disorders that are manifested by progressive neurodegeneration, leading to behavioral and physical impairments. An increased body of evidence suggests that chromatin structure and epigenetic regulation are involved in disease pathology. PolyQ diseases often display an aberrant transcriptional regulation due to the disrupted function of histone-modifying complexes and altered interactions of the polyQ-extended proteins with chromatin-related factors. In this review we describe recent findings relating to the role of chromatin in polyQ diseases. We discuss the involvement of epigenetic-related factors and chromatin structure in genomic instability of CAG repeats; we describe changes in the expression and regulation of chromatin-related enzymes and in the levels and patterns of histone modifications in disease state; we illustrate the potential beneficial effects of different histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors for the treatment of polyQ diseases, and we end by describing the potential use of human pluripotent stem cells and their differentiated derivatives for modeling polyQ diseases in vitro. Taken together, these accumulating studies strongly suggest that disrupted chromatin regulation may be directly involved with the pathophysiology of polyQ-related diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Histone deacetylase inhibitors as therapeutic agents for polyglutamine disorders].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2010 Feb;27(1):52-5. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2010.01.011. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20140868 Review. Chinese.
-
Gene Alterations Induced by Glutamine (Q) Encoding CAG Repeats Associated with Neurodegeneration.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2575:3-23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2716-7_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36301468
-
Sodium valproate alleviates neurodegeneration in SCA3/MJD via suppressing apoptosis and rescuing the hypoacetylation levels of histone H3 and H4.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54792. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054792. Epub 2013 Jan 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23382971 Free PMC article.
-
Deregulation of histone-modifying enzymes and chromatin structure modifiers contributes to glioma development.Future Oncol. 2015 Sep;11(18):2587-601. doi: 10.2217/fon.15.171. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Future Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26289459 Review.
-
Transcriptional Dysregulation and Post-translational Modifications in Polyglutamine Diseases: From Pathogenesis to Potential Therapeutic Strategies.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 May 15;11:153. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00153. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29867345 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hat1 acetylates histone H4 and modulates the transcriptional program in Drosophila embryogenesis.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 29;9(1):17973. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54497-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31784689 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic mechanisms of neurodegenerative diseases and acute brain injury.Neurochem Int. 2020 Feb;133:104642. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2019.104642. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Neurochem Int. 2020. PMID: 31838024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Open chromatin structure in PolyQ disease-related genes: a potential mechanism for CAG repeat expansion in the normal human population.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2019 Jul 30;1(1):e3. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqz003. eCollection 2019 Apr. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 33575550 Free PMC article.
-
The HDAC interaction network.Mol Syst Biol. 2013;9:671. doi: 10.1038/msb.2013.33. Mol Syst Biol. 2013. PMID: 23752267 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Drosophila model of Huntington disease-like 2 exhibits nuclear toxicity and distinct pathogenic mechanisms from Huntington disease.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Aug 1;25(15):3164-3177. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw166. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27288455 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
