The estrogen receptor-α is required and sufficient to maintain physiological glucose uptake in the mouse heart
- PMID: 22892812
- PMCID: PMC4775096
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.190389
The estrogen receptor-α is required and sufficient to maintain physiological glucose uptake in the mouse heart
Abstract
Estrogens attenuate cardiac hypertrophy and increase cardiac contractility via their cognate estrogen receptors (ERs) ERα and ERβ. Because female sex hormones enhance global glucose use and because myocardial function and mass are tightly linked to cardiac glucose metabolism, we tested the hypothesis that expression and activation of the ERα might be required and sufficient to maintain physiological cardiac glucose uptake in the murine heart. Cardiac glucose uptake quantified in vivo by 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography was strongly impaired in ovariectomized compared with gonadal intact female C57BL/6JO mice. The selective ERα agonist 16α-LE2 and the nonselective ERα and ERβ agonist 17β-estradiol completely restored cardiac glucose uptake in ovariectomized mice. Cardiac 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake was strongly decreased in female ERα knockout mice compared with wild-type littermates. Analysis of cardiac mRNA accumulation by quantitative RT-PCR revealed an upregulation of genes involved in glycolisis and tricarboxylic acid cycle by ERα treatment. In conclusion, systemic activation of ERα is sufficient, and its expression is required to maintain physiological glucose uptake in the murine heart, which is likely to contribute to known cardioprotective estrogen effects.
Figures
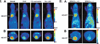
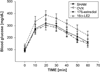
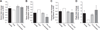
Similar articles
-
Rat uterine oxytocin receptor and estrogen receptor α and β mRNA levels are regulated by estrogen through multiple estrogen receptors.J Reprod Dev. 2014 Mar 7;60(1):55-61. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2012-139. Epub 2013 Dec 16. J Reprod Dev. 2014. PMID: 24334513 Free PMC article.
-
The estrogen receptor-alpha agonist 16alpha-LE2 inhibits cardiac hypertrophy and improves hemodynamic function in estrogen-deficient spontaneously hypertensive rats.Cardiovasc Res. 2005 Sep 1;67(4):604-12. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.04.035. Cardiovasc Res. 2005. PMID: 15950203
-
Contribution of estrogen receptor subtypes, ERα, ERβ, and GPER1 in rapid estradiol-mediated enhancement of hippocampal synaptic transmission in mice.Hippocampus. 2015 Dec;25(12):1556-66. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22475. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Hippocampus. 2015. PMID: 25980457 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of specific target genes and biological responses by estrogen receptor subtype agonists.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010 Dec;10(6):629-36. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2010.09.009. Epub 2010 Oct 14. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20951642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
No detectable changes in anxiety-related and locomotor behaviors in adult ovariectomized female rats exposed to estradiol, the ERβ agonist DPN or the ERα agonist PPT.Horm Behav. 2023 Jun;152:105363. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2023.105363. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Horm Behav. 2023. PMID: 37087765 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An animal model with a cardiomyocyte-specific deletion of estrogen receptor alpha: functional, metabolic, and differential network analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 7;9(7):e101900. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101900. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25000186 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen regulation of protein expression and signaling pathways in the heart.Biol Sex Differ. 2014 Mar 10;5(1):6. doi: 10.1186/2042-6410-5-6. Biol Sex Differ. 2014. PMID: 24612699 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogenic Impact on Cardiac Ischemic/Reperfusion Injury.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2016 Feb;9(1):23-39. doi: 10.1007/s12265-016-9675-3. Epub 2016 Jan 19. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 26786980
-
The effects of oestrogens and their receptors on cardiometabolic health.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017 Jun;13(6):352-364. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.12. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28304393 Review.
-
The Role of 17β-Estradiol and Estrogen Receptors in Regulation of Ca2+ Channels and Mitochondrial Function in Cardiomyocytes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 May 15;10:310. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00310. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31156557 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pare G, Krust A, Karas RH, Dupont S, Aronovitz M, Chambon P, Mendelsohn ME. Estrogen receptor-α mediates the protective effects of estrogen against vascular injury. Circ Res. 2002;31:1087–1092. - PubMed
-
- Donaldson C, Eder S, Baker C, Aronovitz MJ, Weiss AD, Hall-Porter M, Wang F, Ackerman A, Karas RH, Molkentin JD, Patten RD. Estrogen attenuates left ventricular and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by an estrogen receptor-dependent pathway that increases calcineurin degradation. Circ Res. 2009;30:265–275. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scolletta S, Biagioli B. Energetic myocardial metabolism and oxidative stress: let’s make them our friends in the fight against heart failure. Biomed Pharmacother. 2010;64:203–207. - PubMed
-
- Opie LH, Knuuti J. The adrenergic-fatty acid load in heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;27:1637–1646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

