Validation of Polo-like kinase 1 as a therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 22892842
- PMCID: PMC3469479
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.21412
Validation of Polo-like kinase 1 as a therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
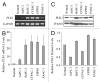
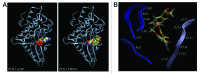
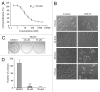
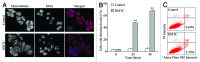
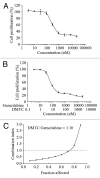
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is a serine/threonine protein kinase and plays a critical role in mitosis. PLK1 has also been regarded as a valuable target for cancer treatment, and several PLK1 inhibitors are currently undergoing clinical investigations. In this study, our data show that the expression level of PLK1 is upregulated in human pancreatic cancer cells. Molecular modeling studies indicate that DMTC inhibits PLK1 activity through competitive displacement of ATP from its binding pocket. Our data further show that DMTC suppresses the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells and induces the formation of multinucleated cells, ultimately resulting in apoptosis. In addition, combination index analysis demonstrates that DMTC acts synergistically with the chemotherapeutic drug gemcitabine in inhibiting the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. These results thus suggest a potential of using PLK1 inhibitors for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Sunkel CE, Glover DM. polo, a mitotic mutant of Drosophila displaying abnormal spindle poles. J Cell Sci. 1988;89:25–38. - PubMed
-
- Burkard ME, Randall CL, Larochelle S, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Fisher RP, et al. Chemical genetics reveals the requirement for Polo-like kinase 1 activity in positioning RhoA and triggering cytokinesis in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:4383–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701140104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
