Negative regulation of osteoclast precursor differentiation by CD11b and β2 integrin-B-cell lymphoma 6 signaling
- PMID: 22893614
- PMCID: PMC3522783
- DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.1739
Negative regulation of osteoclast precursor differentiation by CD11b and β2 integrin-B-cell lymphoma 6 signaling
Abstract
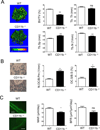
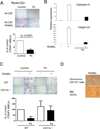
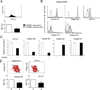
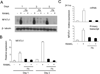
Negative regulation of osteoclastogenesis is important for bone homeostasis and prevention of excessive bone resorption in inflammatory and other diseases. Mechanisms that directly suppress osteoclastogenesis are not well understood. In this study we investigated regulation of osteoclast differentiation by the β2 integrin CD11b/CD18 that is expressed on myeloid lineage osteoclast precursors. CD11b-deficient mice exhibited decreased bone mass that was associated with increased osteoclast numbers and decreased bone formation. Accordingly, CD11b and β2 integrin signaling suppressed osteoclast differentiation by preventing receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced induction of the master regulator of osteoclastogenesis nuclear factor of activated T cells, cytoplasmic 1 (NFATc1) and of downstream osteoclast-related NFATc1 target genes. CD11b suppressed induction of NFATc1 by the complementary mechanisms of downregulation of RANK expression and induction of recruitment of the transcriptional repressor B-cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6) to the NFATC1 gene. These findings identify CD11b as a negative regulator of the earliest stages of osteoclast differentiation, and provide an inducible mechanism by which environmental cues suppress osteoclastogenesis by activating a transcriptional repressor that makes genes refractory to osteoclastogenic signaling.
Copyright © 2013 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors state that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD11b promotes the differentiation of osteoclasts induced by RANKL through the spleen tyrosine kinase signalling pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Dec;21(12):3445-3452. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13254. Epub 2017 Jun 29. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28661042 Free PMC article.
-
Agrimophol suppresses RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis through Blimp1-Bcl6 axis and prevents inflammatory bone loss in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Jan;90:107137. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107137. Epub 2020 Nov 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33199235
-
The Blimp1-Bcl6 axis is critical to regulate osteoclast differentiation and bone homeostasis.J Exp Med. 2010 Apr 12;207(4):751-62. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091957. Epub 2010 Apr 5. J Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 20368579 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances of NFATc1 in rheumatoid arthritis-related bone destruction: mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.Mol Med. 2024 Feb 3;30(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00788-w. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38310228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxic Effects of Indoxyl Sulfate on Osteoclastogenesis and Osteoblastogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 19;22(20):11265. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011265. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681927 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The current status of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies and citrullinated protein-reactive B cells in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Mar;49(3):2475-2485. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-07034-0. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34855107 Review.
-
Macrophage Infiltration and ITGB2 Expression in ESCC: A Novel Correlation.Cancer Med. 2025 Jan;14(2):e70604. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70604. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 39825491 Free PMC article.
-
β2 Integrins-Multi-Functional Leukocyte Receptors in Health and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 19;21(4):1402. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041402. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32092981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory Effect of Purpurogallin on Osteoclast Differentiation in Vitro through the Downregulation of c-Fos and NFATc1.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 17;19(2):601. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020601. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29463002 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of the Association of Fibrinogen Citrullination and Osteoclastogenesis in Bone Destruction in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Cells. 2020 Dec 20;9(12):2720. doi: 10.3390/cells9122720. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33419308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arai F, Miyamoto T, Ohneda O, Inada T, Sudo T, Brasel K, Miyata T, Anderson DM, Suda T. Commitment and differentiation of osteoclast precursor cells by the sequential expression of c-Fms and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB (RANK) receptors. J Exp Med. 1999;190(12):1741–1754. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Novack DV, Teitelbaum SL. The osteoclast: friend or foe? Annu Rev Pathol. 2008;3:457–484. - PubMed
-
- Walsh MC, Kim N, Kadono Y, Rho J, Lee SY, Lorenzo J, Choi Y. Osteoimmunology: interplay between the immune system and bone metabolism. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:33–63. - PubMed
-
- Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H, Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T, Inoue J, Wagner EF, Mak TW, Kodama T, Taniguchi T. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 2002;3(6):889–901. - PubMed
-
- Mocsai A, Humphrey MB, Van Ziffle JA, Hu Y, Burghardt A, Spusta SC, Majumdar S, Lanier LL, Lowell CA, Nakamura MC. The immunomodulatory adapter proteins DAP12 and Fc receptor gamma-chain (FcRgamma) regulate development of functional osteoclasts through the Syk tyrosine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(16):6158–6163. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

