Current management of parainfluenza pneumonitis in immunocompromised patients: a review
- PMID: 22893749
- PMCID: PMC3418768
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S25874
Current management of parainfluenza pneumonitis in immunocompromised patients: a review
Abstract
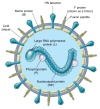
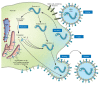
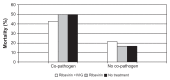
Parainfluenza viruses (PIV) are common respiratory viruses that belong to the Paramyxoviridae family. PIV infection can lead to a wide variety of clinical syndromes ranging from mild upper respiratory illness to severe pneumonia. Severe disease can be seen in elderly or chronically ill persons and may be fatal in persons with compromised immune systems, particularly children with severe combined immunodeficiency disease syndrome and hematopathic stem cell transplant recipients. At present, there are no licensed antiviral agents for the treatment of PIV infection. Aerosolized or systemic ribavirin in combination with intravenous gamma globulin has been reported in small, uncontrolled series and case reports of immunocompromised patients. A number of agents show antiviral activity in vitro and in animals, but none are currently approved for human use.
Keywords: antiviral agents; immunocompromised host; parainfluenza virus.
Figures
References
-
- Hall CB. Respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza virus. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(25):1917–1928. - PubMed
-
- Stankova J, Carret AS, Moore D, et al. Long-term therapy with aerosolized ribavirin for parainfluenza 3 virus respiratory tract infection in an infant with severe combined immunodeficiency. Pediatr Transplant. 2007;11(2):209–213. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

