High performance lung nodule detection schemes in CT using local and global information
- PMID: 22894441
- PMCID: PMC4108707
- DOI: 10.1118/1.4737109
High performance lung nodule detection schemes in CT using local and global information
Abstract
Purpose: A key issue in current computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) schemes for nodule detection in CT is the large number of false positives, because current schemes use only global three-dimensional (3D) information to detect nodules and discard useful local two-dimensional (2D) information. Thus, the authors integrated local and global information to markedly improve the performance levels of CAD schemes.
Methods: Our database was obtained from the standard CT lung nodule database created by the Lung Image Database Consortium (LIDC). It consisted of 85 CT scans with 111 nodules of 3 mm or larger in diameter. The 111 nodules were confirmed by at least two of the four radiologists participated in the LIDC. Twenty-six nodules were missed by two of the four radiologists and were thus very difficult to detect. The authors developed five CAD schemes for nodule detection in CT using global 3D information (3D scheme), local 2D information (2D scheme), and both local and global information (2D + 3D scheme, 2D - 3D scheme, and 3D - 2D scheme). The 3D scheme, which was developed previously, used only global 3D information and discarded local 2D information, as other CAD schemes did. The 2D scheme used a uniform viewpoint reformation technique to decompose a 3D nodule candidate into a set of 2D reformatted images generated from representative viewpoints, and selected and used "effective" 2D reformatted images to remove false positives. The 2D + 3D scheme, 2D - 3D scheme, and 3D - 2D scheme used complementary local and global information in different ways to further improve the performance of lung nodule detection. The authors employed a leave-one-scan-out testing method for evaluation of the performance levels of the five CAD schemes.
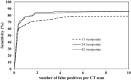
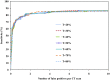
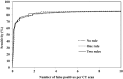
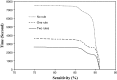
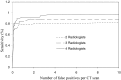
Results: At the sensitivities of 85%, 80%, and 75%, the existing 3D scheme reported 17.3, 7.4, and 2.8 false positives per scan, respectively; the 2D scheme improved the detection performance and reduced the numbers of false positives to 7.6, 2.5, and 1.3 per scan; the 2D + 3D scheme further reduced those to 2.7, 1.9, and 0.6 per scan; the 2D - 3D scheme reduced those to 7.6, 2.1, and 0.8 per scan; and the 3D - 2D scheme reduced those to 17.3, 1.6, and 1.0 per scan.
Conclusions: The local 2D information appears to be more useful than the global 3D information for nodule detection, particularly, when it is integrated with 3D information.
Figures






References
-
- Roos J. E., Paik D., Olsen D., Chow L. C., Leung A. N., Mindelzun R., Choudhury K. R., Naidich D. P., Napel S., and Rubin G. D., “Computer-aided detection (CAD) of lung nodules in CT scans: Radiologist performance and reading time with incremental CAD assistance,” Eur. Radiol. 20(3), 549–557 (2010). 10.1007/s00330-009-1596-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beyer F., Zierott L., Fallenberg E. M., Juergens K. U., Stoeckel J., Heindel W., and Wormanns D., “Comparison of sensitivity and reading time for the use of computer-aided detection (CAD) of pulmonary nodules at MDCT as concurrent or second reader,” Eur. Radiol. 17(11), 2941–2947 (2007). 10.1007/s00330-007-0667-1 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

