Molecular imaging of water binding state and diffusion in breast cancer using diffuse optical spectroscopy and diffusion weighted MRI
- PMID: 22894465
- PMCID: PMC3381027
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JBO.17.7.071304
Molecular imaging of water binding state and diffusion in breast cancer using diffuse optical spectroscopy and diffusion weighted MRI
Abstract
Tissue water content and molecular microenvironment can provide important intrinsic contrast for cancer imaging. In this work, we examine the relationship between water optical spectroscopic features related to binding state and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-measured water diffusion dynamics. Broadband diffuse optical spectroscopic imaging (DOSI) and MR images were obtained from eight patients with locally-advanced infiltrating ductal carcinomas (tumor size=5.5 ± 3.2 cm). A DOSI-derived bound water index (BWI) was compared to the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of diffusion weighted (DW) MRI. BWI and ADC were positively correlated (R=0.90, p-value=0.003) and BWI and ADC both decreased as the bulk water content increased (R=-0.81 and -0.89, respectively). BWI correlated inversely with tumor size (R=-0.85, p-value=0.008). Our results suggest underlying sensitivity differences between BWI and ADC to water in different tissue compartments (e.g., extracellular vs cellular). These data highlight the potential complementary role of DOSI and DW-MRI in providing detailed information on the molecular disposition of water in breast tumors. Because DOSI is a portable technology that can be used at the bedside, BWI may provide a low-cost measure of tissue water properties related to breast cancer biology.
Figures
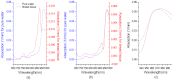


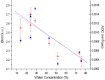
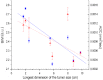
References
-
- Sickles E. A., “Breast masses: mammographic evaluation,” Radiology 173(2), 297–303 (1989). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 CA142989/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009054/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54-CA105480/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA105480/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA142989/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA136400/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NCI-2P30CA62203/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NCI-T32CA009054/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54-CA136400/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41-RR01192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR001192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA062203/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States

