Peptide vaccines and targeting HER and VEGF proteins may offer a potentially new paradigm in cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 22894670
- PMCID: PMC4591923
- DOI: 10.2217/fon.12.95
Peptide vaccines and targeting HER and VEGF proteins may offer a potentially new paradigm in cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
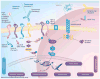
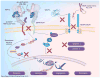
The ErbB family (HER-1, HER-2, HER-3 and HER-4) of receptor tyrosine kinases has been the focus of cancer immunotherapeutic strategies while antiangiogenic therapies have focused on VEGF and its receptors VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2. Agents targeting receptor tyrosine kinases in oncology include therapeutic antibodies to receptor tyrosine kinase ligands or the receptors themselves, and small-molecule inhibitors. Many of the US FDA-approved therapies targeting HER-2 and VEGF exhibit unacceptable toxicities, and show problems of efficacy, development of resistance and unacceptable safety profiles that continue to hamper their clinical progress. The combination of different peptide vaccines and peptidomimetics targeting specific molecular pathways that are dysregulated in tumors may potentiate anticancer immune responses, bypass immune tolerance and circumvent resistance mechanisms. The focus of this review is to discuss efforts in our laboratory spanning two decades of rationally developing peptide vaccines and therapeutics for breast cancer. This review highlights the prospective benefit of a new, untapped category of therapies biologically targeted to EGF receptor (HER-1), HER-2 and VEGF with potential peptide 'blockbusters' that could lay the foundation of a new paradigm in cancer immunotherapy by creating clinical breakthroughs for safe and efficacious cancer cures.
Figures




Similar articles
-
B-cell epitope peptide cancer vaccines: a new paradigm for combination immunotherapies with novel checkpoint peptide vaccine.Future Oncol. 2020 Aug;16(23):1767-1791. doi: 10.2217/fon-2020-0224. Epub 2020 Jun 21. Future Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32564612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delayed tumor onset and reduced tumor growth progression after immunization with a Her-2/neu multi-peptide vaccine and IL-12 in c-neu transgenic mice.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007 Nov;106(1):29-38. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9469-4. Epub 2007 Jan 3. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007. PMID: 17203384
-
A paradigm shift: Cancer therapy with peptide-based B-cell epitopes and peptide immunotherapeutics targeting multiple solid tumor types: Emerging concepts and validation of combination immunotherapy.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(6):1368-86. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1026495. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015. PMID: 25874884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy against angiogenesis-associated targets: evidence and implications for the treatment of malignant glioma.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2008 May;8(5):717-32. doi: 10.1586/14737140.8.5.717. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18471045 Review.
-
Cell signalling: growth factors and tyrosine kinase receptors.Clin Transl Oncol. 2006 Feb;8(2):77-82. doi: 10.1007/s12094-006-0162-1. Clin Transl Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16632420 Review.
Cited by
-
A systematic review of vascular endothelial growth factor expression as a biomarker of prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma.Tumour Biol. 2013 Jun;34(3):1895-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0733-z. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23589053
-
Association of the vascular endothelial growth factor -2578C/A polymorphism with cancer risk: A meta-analysis update.Biomed Rep. 2014 Nov;2(6):823-830. doi: 10.3892/br.2014.317. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Biomed Rep. 2014. PMID: 25279153 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Applications of Retro-Inverso Peptides.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 12;22(16):8677. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168677. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HER2-positive gastric cancer: from targeted therapy to CAR-T cell therapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 13;16:1560280. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1560280. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40181988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of cell adhesion and immune responses in the mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis with a peptidomimetic that blocks CD2-CD58 interface interactions.Biopolymers. 2015 Nov;104(6):733-42. doi: 10.1002/bip.22692. Biopolymers. 2015. PMID: 26031942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hynes NE, Lane HA. ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:341–354. - PubMed
-
- Vinter-Jensen L. Pharmacological effects of epidermal growth factor (EGF) with focus on the urinary and gastrointestinal tracts. APMIS Suppl. 1999;93:1–42. - PubMed
-
- Arteaga CL, Moulder SL, Yakes FM. HER (erbB) tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 2002;29:4–10. - PubMed
-
- Barbacci EG, Guarino BC, Stroh JG, et al. The structural basis for the specificity of epidermal growth factor and heregulin binding. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:9585–9589. - PubMed
Websites
-
- American Cancer Society. www.cancer.org.
-
- A Study to Evaluate Pertuzumab + Trastuzumab + Docetaxel vs. Placebo + Trastuzumab + Docetaxel in Previously Untreated Her2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer (CLEOPATRA) http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00567190?term=NCT00567190&rank=1.
-
- Vaccine Therapy in Treating Patients With Metastatic Solid Tumors. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01376505?term=NCT+01376505&rank=1.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
