Epigenetics within the matrix: a neo-regulator of fibrotic disease
- PMID: 22894907
- PMCID: PMC3515019
- DOI: 10.4161/epi.21567
Epigenetics within the matrix: a neo-regulator of fibrotic disease
Abstract
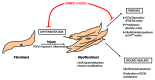
Fibrosis of any tissue is characterized by excessive extracellular matrix accumulation that ultimately destroys tissue architecture and eventually abolishes normal organ function. Although much research has focused on the mechanisms underlying disease pathogenesis, there are still no effective antifibrotic therapies that can reverse, stop or delay the formation of scar tissue in most fibrotic organs. As fibrosis can be described as an aberrant wound healing response, a recent hypothesis suggests that the cells involved in this process gain an altered heritable phenotype that promotes excessive fibrotic tissue accumulation. This article will review the most recent observations in a newly emerging field that links epigenetic modifications to the pathogenesis of fibrosis. Specifically, the roles of DNA methylation and histone modifications in fibrotic disease will be discussed.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
