Respiratory syncytial virus modifies microRNAs regulating host genes that affect virus replication
- PMID: 22894925
- PMCID: PMC3542124
- DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.044255-0
Respiratory syncytial virus modifies microRNAs regulating host genes that affect virus replication
Abstract
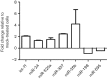
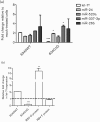
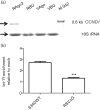
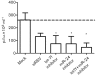
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes substantial morbidity and life-threatening lower respiratory tract disease in infants, young children and the elderly. Understanding the host response to RSV infection is critical for developing disease-intervention approaches. The role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in post-transcriptional regulation of host genes responding to RSV infection is not well understood. In this study, it was shown that RSV infection of a human alveolar epithelial cell line (A549) induced five miRNAs (let-7f, miR-24, miR-337-3p, miR-26b and miR-520a-5p) and repressed two miRNAs (miR-198 and miR-595), and showed that RSV G protein triggered let-7f expression. Luciferase-untranslated region reporters and miRNA mimics and inhibitors validated the predicted targets, which included cell-cycle genes (CCND1, DYRK2 and ELF4), a chemokine gene (CCL7) and the suppressor of cytokine signalling 3 gene (SOCS3). Modulating let-7 family miRNA levels with miRNA mimics and inhibitors affected RSV replication, indicating that RSV modulates host miRNA expression to affect the outcome of the antiviral host response, and this was mediated in part through RSV G protein expression.
Figures

References
-
- Alvarez R., Elbashir S., Borland T., Toudjarska I., Hadwiger P., John M., Roehl I., Morskaya S. S., Martinello R. & other authors (2009). RNA interference-mediated silencing of the respiratory syncytial virus nucleocapsid defines a potent antiviral strategy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53, 3952–3962 10.1128/AAC.00014-09 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Becker Y. (2006). Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) evades the human adaptive immune system by skewing the Th1/Th2 cytokine balance toward increased levels of Th2 cytokines and IgE, markers of allergy – a review. Virus Genes 33, 235–252 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

