The BTB-ZF transcription factors
- PMID: 22894929
- PMCID: PMC3466544
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.21277
The BTB-ZF transcription factors
Abstract
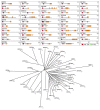
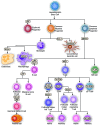
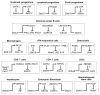
The BTB-ZF (broad-complex, tramtrack and bric-à-brac--zinc finger) proteins are encoded by at least 49 genes in mouse and man and commonly serve as sequence-specific silencers of gene expression. This review will focus on the known physiological functions of mammalian BTB-ZF proteins, which include essential roles in the development of the immune system. We discuss their function in terminally differentiated lymphocytes and the progenitors that give rise to them, their action in hematopoietic malignancy and roles beyond the immune system.
Figures

References
-
- Godt D, Couderc JL, Cramton SE, Laski FA. Pattern formation in the limbs of Drosophila: bric à brac is expressed in both a gradient and a wave-like pattern and is required for specification and proper segmentation of the tarsus. Development. 1993;119:799–812. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
