Spartan/C1orf124 is important to prevent UV-induced mutagenesis
- PMID: 22894931
- PMCID: PMC3466550
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.21694
Spartan/C1orf124 is important to prevent UV-induced mutagenesis
Abstract
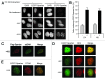
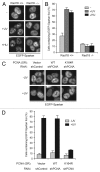
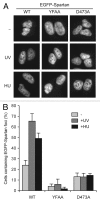
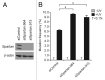
Uninterrupted replication across damaged DNA is critical to prevent replication fork collapse and resulting double-strand DNA breaks. Rad18-mediated PCNA ubiquitination is a crucial event that triggers a number of downstream pathways important for lesion bypass. Here, we report characterization of Spartan, an evolutionarily conserved protein containing a PCNA-interacting peptide motif, called a PIP box, and a UBZ4 ubiquitin-binding domain. Spartan is a nuclear protein and forms DNA damage-induced foci that colocalize with markers for stalled DNA replication. Focus formation of Spartan requires its PIP-box and the UBZ4 domain and is dependent on Rad18 and the PCNA ubiquitination site, indicating that Spartan is recruited to ubiquitinated PCNA. Spartan depletion results in increased mutagenesis during replication of UV-damaged DNA. Taken together, our data suggest that Spartan is recruited to sites of stalled replication via ubiquitinated PCNA and plays an important role to prevent mutations associated with replication of damaged DNA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spartan/C1orf124, a reader of PCNA ubiquitylation and a regulator of UV-induced DNA damage response.Mol Cell. 2012 Jun 8;46(5):625-35. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.05.020. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22681887 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of human Spartan/C1orf124, an ubiquitin-PCNA interacting regulator of DNA damage tolerance.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Nov;40(21):10795-808. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks850. Epub 2012 Sep 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22987070 Free PMC article.
-
DVC1 (C1orf124) is a DNA damage-targeting p97 adaptor that promotes ubiquitin-dependent responses to replication blocks.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Nov;19(11):1084-92. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2395. Epub 2012 Oct 7. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23042605
-
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)-binding protein C1orf124 is a regulator of translesion synthesis.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 5;287(41):34225-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.400135. Epub 2012 Aug 17. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22902628 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of DNA damage tolerance in mammalian cells by post-translational modifications of PCNA.Mutat Res. 2017 Oct;803-805:82-88. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2017.06.004. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Mutat Res. 2017. PMID: 28666590 Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of VCP/UFD1/Nucleolin in the viral entry of Enterovirus A species.Virus Res. 2020 Jul 2;283:197974. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.197974. Epub 2020 Apr 11. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32289342 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Haploid, a Metalloprotease Enriched at the Largest Satellite Repeat and Essential for Genome Integrity in Drosophila Embryos.Genetics. 2017 Aug;206(4):1829-1839. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.200949. Epub 2017 Jun 14. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28615282 Free PMC article.
-
Strategic role of the ubiquitin-dependent segregase p97 (VCP or Cdc48) in DNA replication.Chromosoma. 2017 Feb;126(1):17-32. doi: 10.1007/s00412-016-0587-4. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Chromosoma. 2017. PMID: 27086594 Review.
-
Translesion Synthesis or Repair by Specialized DNA Polymerases Limits Excessive Genomic Instability upon Replication Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 10;22(8):3924. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083924. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33920223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The protease SPRTN and SUMOylation coordinate DNA-protein crosslink repair to prevent genome instability.Cell Rep. 2021 Dec 7;37(10):110080. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110080. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34879279 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
