Towards recyclable NAD(P)H regeneration catalysts
- PMID: 22895028
- PMCID: PMC6268897
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules17089835
Towards recyclable NAD(P)H regeneration catalysts
Abstract
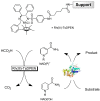
Rh(III)-TsDPEN, an immobilized analog of the well-known [Cp*Rh(bpy)(H(2)O)](2+) was evaluated as a heterogeneous, recyclable regeneration catalyst for reduced oxidoreductase cofactors [NAD(P)H]. Repeated use of this catalyst was established and the catalytic properties were initially investigated. Apparently, Rh(III)-TsDPEN is prone to severe diffusion limitations, necessitating further developments. Overall, a promising concept for chemoenzymatic redox catalysis is proposed, which may overcome some of the current limitations such as catalyst cost and incompatibility of Rh with some biocatalysts.
Figures
 ; 2:
; 2: ; 3:
; 3: ; 4:
; 4: ; 5:
; 5: ; 6:
; 6: ; 7:
; 7: ; 8:
; 8: ; 9:
; 9: ; 10:
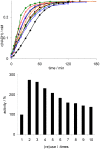
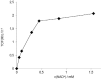
; 10: ); lower: initial rates. Conditions: 50 mg Rh(III)-TsDPEN (0.35 μmol), c(NAD+)0 = 0.25 mM, 50 mM phosphate buffer pH 7, T = 30 °C, c(NaHCO2) = 150 mM, 1,000 rpm; 100% corresponds to an NADH-generation rate of 0.21 mM·h−1.
); lower: initial rates. Conditions: 50 mg Rh(III)-TsDPEN (0.35 μmol), c(NAD+)0 = 0.25 mM, 50 mM phosphate buffer pH 7, T = 30 °C, c(NaHCO2) = 150 mM, 1,000 rpm; 100% corresponds to an NADH-generation rate of 0.21 mM·h−1.
References
-
- Hollmann F., Arends I.W.C.E., Buehler K. Biocatalytic Redox Reactions for Organic Synthesis: Nonconventional Regeneration Methods. ChemCatChem. 2010;2:762–782. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201000069. - DOI
-
- Song H.K., Lee S.H., Won K., Park J.H., Kim J.K., Lee H., Moon S.J., Kim D.K., Park C.B. Electrochemical regeneration of NADH enhanced by platinum nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008;47:1749–1752. - PubMed
-
- Kim J.H., Lee S.H., Lee J.S., Lee M., Park C.B. Zn-containing porphyrin as a biomimetic light-harvesting molecule for biocatalyzed artificial photosynthesis. Chem. Commun. 2011;47:10227–10229. - PubMed
-
- Kim J.H., Lee M., Lee J.S., Park C.B. Self-Assembled Light-Harvesting Peptide Nanotubes for Mimicking Natural Photosynthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012;51:517–520. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

