Potential applications of bacteriorhodopsin mutants
- PMID: 22895057
- PMCID: PMC3489707
- DOI: 10.4161/bioe.21445
Potential applications of bacteriorhodopsin mutants
Abstract
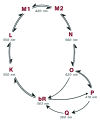
Bacteriorhodopsin (BR), a model system in biotechnology, is a G-protein dependent trans membrane protein which serves as a light driven proton pump in the cell membrane of Halobacterium salinarum. Due to the linkage of retinal to the protein, it seems colored and has numbers of versatile properties. As in vitro culture of the Halobacteria is very difficult, and isolation is time consuming and usually inefficient, production of genetically modified constructs of the protein is essential. There are three important characteristics based on protein catalytic cycle and molecular functions of photo-electric, photochromic and proton transporting, which makes this protein as a strategic molecule with potential applications in biotechnology. Such applications include protein films, used in artificial retinal implants, light modulators, three-dimensional optical memories, color photochromic sensors, photochromic and electrochromic papers and ink, biological camouflage and photo detectors for biodefense and non-defense purposes.
Figures
References
-
- Korposh SO. Development of sensitive elements based on photochromic bacteriorhodopsin for fiber optic sensors. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2007;133:281–90. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2008.02.038. - DOI
-
- Chen Zh, Birge RR. Protein-based artificial retinas, Pub. 2010; US2010/0226957A1. - PubMed
-
- Brauchle C, Hampp N, Oesterhelt D. Optical applications of bacteriorhodopsin and its mutated variants. Adv Mater (Deerfield Beach Fla) 1991;3:420–8. doi: 10.1002/adma.19910030903. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials