Ethanol stimulates epithelial sodium channels by elevating reactive oxygen species
- PMID: 22895258
- PMCID: PMC3530770
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00139.2012
Ethanol stimulates epithelial sodium channels by elevating reactive oxygen species
Abstract
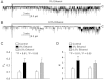
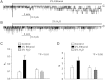
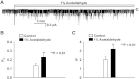
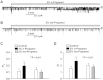
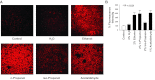
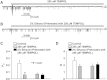
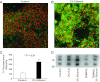
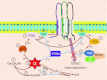
Alcohol affects total body sodium balance, but the molecular mechanism of its effect remains unclear. We used single-channel methods to examine how ethanol affects epithelial sodium channels (ENaC) in A6 distal nephron cells. The data showed that ethanol significantly increased both ENaC open probability (P(o)) and the number of active ENaC in patches (N). 1-Propanol and 1-butanol also increased ENaC activity, but iso-alcohols did not. The effects of ethanol were mimicked by acetaldehyde, the first metabolic product of ethanol, but not by acetone, the metabolic product of 2-propanol. Besides increasing open probability and apparent density of active channels, confocal microscopy and surface biotinylation showed that ethanol significantly increased α-ENaC protein in the apical membrane. The effects of ethanol on ENaC P(o) and N were abolished by a superoxide scavenger, 4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinyloxy (TEMPOL) and blocked by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002. Consistent with an effect of ethanol-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) on ENaC, primary alcohols and acetaldehyde elevated intracellular ROS, but secondary alcohols did not. Taken together with our previous finding that ROS stimulate ENaC, the current results suggest that ethanol stimulates ENaC by elevating intracellular ROS probably via its metabolic product acetaldehyde.
Figures

Comment in
-
Intoxicated Na(+) channels. Focus on "ethanol stimulates epithelial sodium channels by elevating reactive oxygen species".Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 Dec 1;303(11):C1125-6. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00301.2012. Epub 2012 Sep 19. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22992679 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Assadi FK. Acute effect of ethanol on renal electrolyte excretion in rats. Alcohol 6: 257–260, 1989 - PubMed
-
- Bailey SM, Cunningham CC. Acute and chronic ethanol increases reactive oxygen species generation and decreases viability in fresh, isolated rat hepatocytes. Hepatology 28: 1318–1326, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Castellano E, Downward J. Role of RAS in the regulation of PI 3-kinase. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 346: 143–169, 2010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

