The oesophageal string test: a novel, minimally invasive method measures mucosal inflammation in eosinophilic oesophagitis
- PMID: 22895393
- PMCID: PMC3786608
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303171
The oesophageal string test: a novel, minimally invasive method measures mucosal inflammation in eosinophilic oesophagitis
Abstract
Objective: Eosinophil predominant inflammation characterises histological features of eosinophilic oesophagitis (EoE). Endoscopy with biopsy is currently the only method to assess oesophageal mucosal inflammation in EoE. We hypothesised that measurements of luminal eosinophil-derived proteins would correlate with oesophageal mucosal inflammation in children with EoE.
Design: The Enterotest diagnostic device was used to develop an oesophageal string test (EST) as a minimally invasive clinical device. EST samples and oesophageal mucosal biopsies were obtained from children undergoing upper endoscopy for clinically defined indications. Eosinophil-derived proteins including eosinophil secondary granule proteins (major basic protein-1, eosinophil-derived neurotoxin, eosinophil cationic protein, eosinophil peroxidase) and Charcot-Leyden crystal protein/galectin-10 were measured by ELISA in luminal effluents eluted from ESTs and extracts of mucosal biopsies.
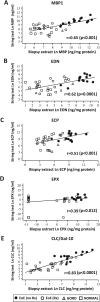
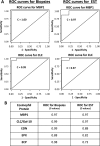
Results: ESTs were performed in 41 children with active EoE (n=14), EoE in remission (n=8), gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (n=4) and controls with normal oesophagus (n=15). EST measurement of eosinophil-derived protein biomarkers significantly distinguished between children with active EoE, treated EoE in remission, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and normal oesophagus. Levels of luminal eosinophil-derived proteins in EST samples significantly correlated with peak and mean oesophageal eosinophils/high power field (HPF), eosinophil peroxidase indices and levels of the same eosinophil-derived proteins in extracts of oesophageal biopsies.
Conclusions: The presence of eosinophil-derived proteins in luminal secretions is reflective of mucosal inflammation in children with EoE. The EST is a novel, minimally invasive device for measuring oesophageal eosinophilic inflammation in children with EoE.
Keywords: Eosinophil; allergy; breast milk; childhood nutrition; enterotest string test; epithelial barrier; gastrointestinal tract; inflammation; oesophageal disease; oesophageal disorders; oesophageal lesions; oesophageal reflux; oesophageal strictures; oesophagitis; pediatric.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology 2007;133:1342–63 - PubMed
-
- Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011;128:3–20 e6 - PubMed
-
- Mueller S, Neureiter D, Aigner T, et al. Comparison of histological parameters for the diagnosis of eosinophilic oesophagitis versus gastro-oesophageal reflux disease on oesophageal biopsy material. Histopathology 2008;53:676–84 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000154/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025741/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1UL1RR025741/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008497/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K26 RR0109709/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL058732/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R21AI079925/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL058732/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI079925/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL058723/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065228/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK067009/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
