Tissue-specific insulin signaling, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 22895666
- PMCID: PMC3511859
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.241919
Tissue-specific insulin signaling, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease
Abstract
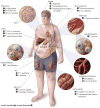
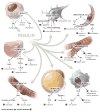
Impaired insulin signaling is central to development of the metabolic syndrome and can promote cardiovascular disease indirectly through development of abnormal glucose and lipid metabolism, hypertension, and a proinflammatory state. However, insulin's action directly on vascular endothelium, atherosclerotic plaque macrophages, and in the heart, kidney, and retina has now been described, and impaired insulin signaling in these locations can alter progression of cardiovascular disease in the metabolic syndrome and affect development of microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus. Recent advances in our understanding of the complex pathophysiology of insulin's effects on vascular tissues offer new opportunities for preventing these cardiovascular disorders.
Figures
References
-
- Olshansky SJ, Passaro DJ, Hershow RC, Layden J, Carnes BA, Brody J, Hayflick L, Butler RN, Allison DB, Ludwig DS. A potential decline in life expectancy in the United States in the 21st century. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1138–1145. - PubMed
-
- Reaven GM. The metabolic syndrome: time to get off the merry-go-round? J Intern Med. 2011;269:127–136. - PubMed
-
- Donath MY, Shoelson SE. Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:98–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK055545/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK085610/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- EY018677/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DK31036/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK033201/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 EY018677/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DK55545/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK082659/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK33201/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK82659/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK031036/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24DK085610/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK031036/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

