A retinal ganglion cell that can signal irradiance continuously for 10 hours
- PMID: 22895730
- PMCID: PMC3432977
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1423-12.2012
A retinal ganglion cell that can signal irradiance continuously for 10 hours
Abstract
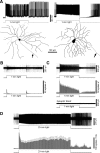
A recently discovered type of mammalian retinal ganglion cell encodes environmental light intensity and mediates non-image-forming visual behaviors, such as the pupillary reflex and circadian photoentrainment. These intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs) generate endogenous, melanopsin-based photoresponses as well as extrinsic, rod/cone-driven responses. Because the ipRGCs' light responses and the behaviors they control are both remarkably tonic, these cells have been hypothesized to be capable of irradiance detection lasting throughout the day. I tested this hypothesis by obtaining multielectrode-array recordings from ipRGCs in a novel rat eyecup preparation that enhances the regeneration of rod/cone photopigments. I found that 10 h constant light could continuously evoke action potentials in these ganglion cells under conditions that stimulated (1) only melanopsin, (2) mainly the rod input, and (3) both intrinsic and extrinsic responses. In response to a 10 h stimulus with gradual intensity changes to simulate sunrise and sunset, ipRGC firing rates slowly increased during the "sunrise" phase and slowly decreased during the "sunset" phase. Furthermore, I recorded from putative ipRGCs of melanopsin-knock-out mice and found that these cells retained the ability to respond in a sustained fashion to 20 min light steps, indicating that melanopsin is not required for such tonic responses. In conclusion, ipRGCs can signal light continuously for at least 10 h and can probably track gradual irradiance changes over the course of the day. These results further suggest that the photoreceptors and ON bipolar cells presynaptic to ipRGCs may be able to respond to light continuously for 10 h.
Figures
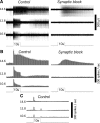
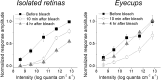
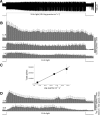
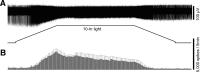
References
-
- Berson DM, Dunn FA, Takao M. Phototransduction by retinal ganglion cells that set the circadian clock. Science. 2002;295:1070–1073. - PubMed
-
- Dacey DM, Liao HW, Peterson BB, Robinson FR, Smith VC, Pokorny J, Yau KW, Gamlin PD. Melanopsin-expressing ganglion cells in primate retina signal colour and irradiance and project to the LGN. Nature. 2005;433:749–754. - PubMed
-
- DeVries SH, Schwartz EA. Kainate receptors mediate synaptic transmission between cones and ‘Off’ bipolar cells in a mammalian retina. Nature. 1999;397:157–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
